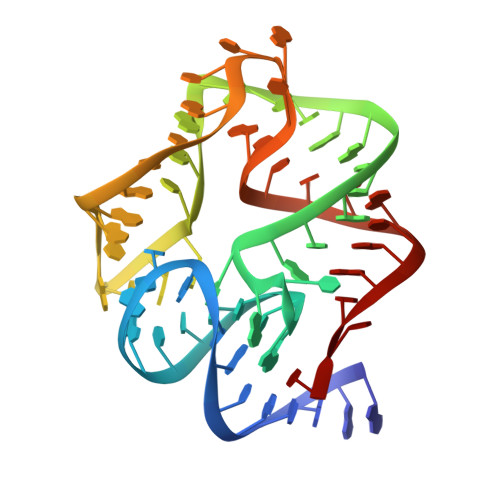
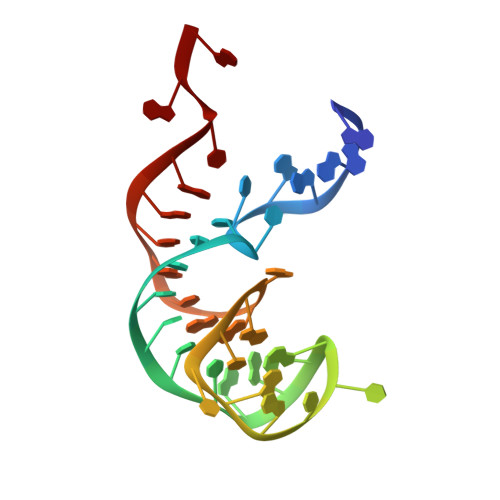
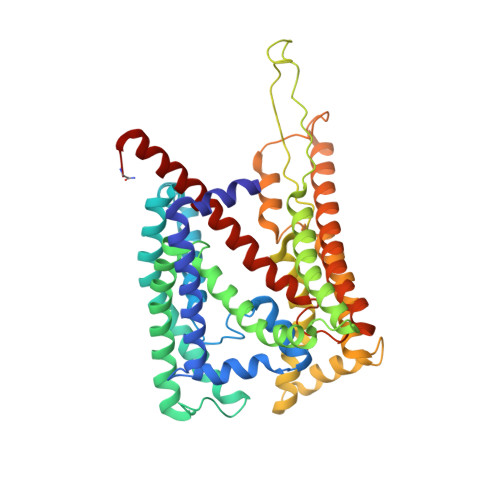
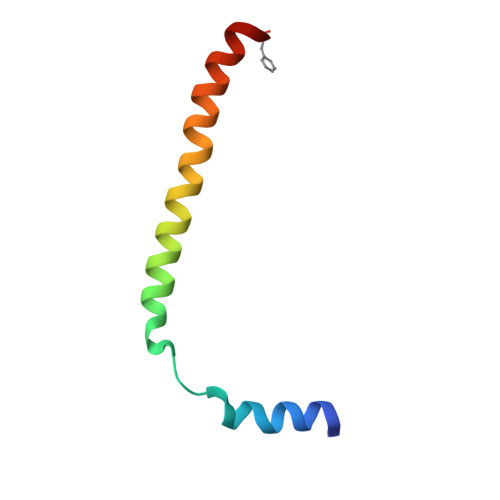
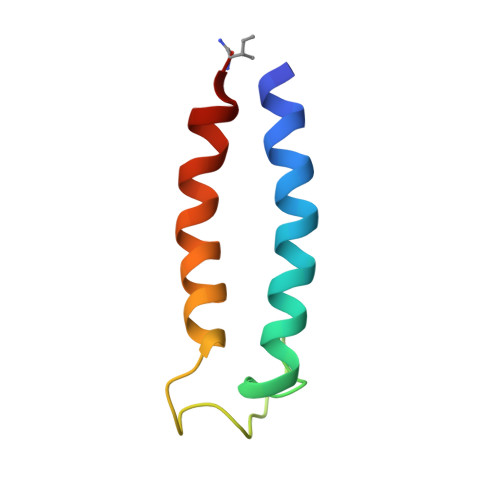
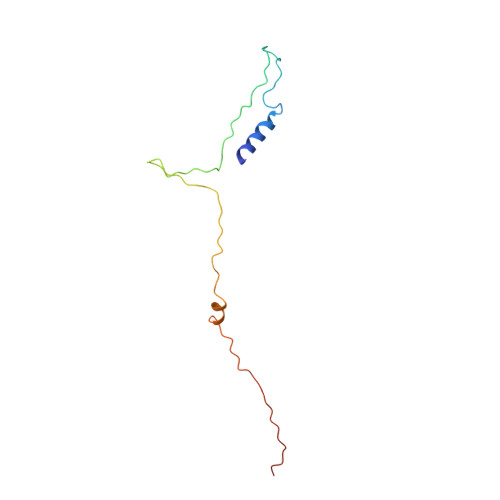
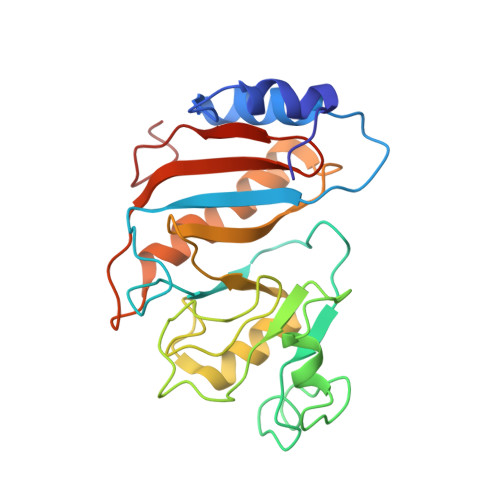
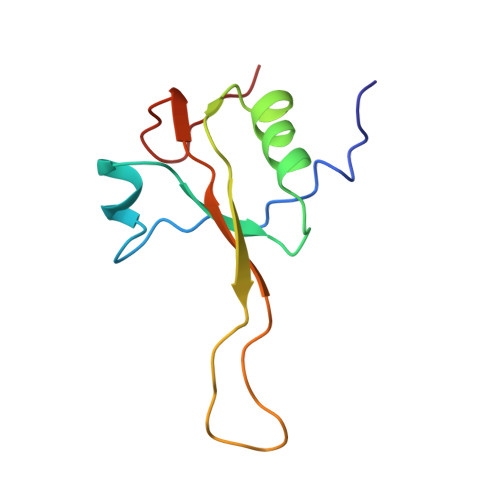
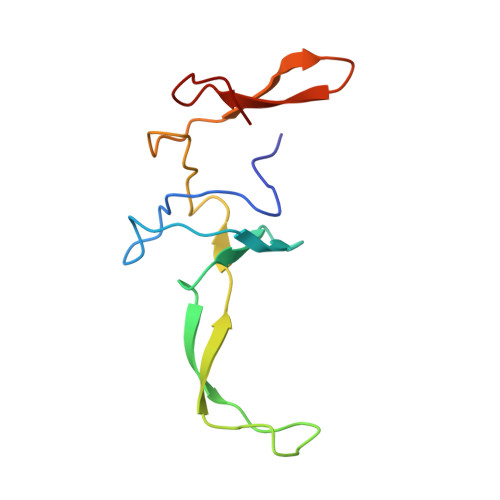
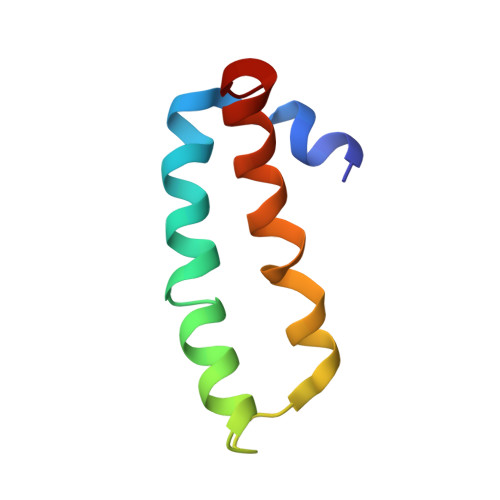
Structure of the SecY channel during initiation of protein translocation.
Park, E., Menetret, J.F., Gumbart, J.C., Ludtke, S.J., Li, W., Whynot, A., Rapoport, T.A., Akey, C.W.(2013) Nature 506: 102-106
- PubMed: 24153188
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12720
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3J45, 3J46, 4V4N - PubMed Abstract:
Many secretory proteins are targeted by signal sequences to a protein-conducting channel, formed by prokaryotic SecY or eukaryotic Sec61 complexes, and are translocated across the membrane during their synthesis. Crystal structures of the inactive channel show that the SecY subunit of the heterotrimeric complex consists of two halves that form an hourglass-shaped pore with a constriction in the middle of the membrane and a lateral gate that faces the lipid phase. The closed channel has an empty cytoplasmic funnel and an extracellular funnel that is filled with a small helical domain, called the plug. During initiation of translocation, a ribosome-nascent chain complex binds to the SecY (or Sec61) complex, resulting in insertion of the nascent chain. However, the mechanism of channel opening during translocation is unclear. Here we have addressed this question by determining structures of inactive and active ribosome-channel complexes with cryo-electron microscopy. Non-translating ribosome-SecY channel complexes derived from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii or Escherichia coli show the channel in its closed state, and indicate that ribosome binding per se causes only minor changes. The structure of an active E. coli ribosome-channel complex demonstrates that the nascent chain opens the channel, causing mostly rigid body movements of the amino- and carboxy-terminal halves of SecY. In this early translocation intermediate, the polypeptide inserts as a loop into the SecY channel with the hydrophobic signal sequence intercalated into the open lateral gate. The nascent chain also forms a loop on the cytoplasmic surface of SecY rather than entering the channel directly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cell Biology and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard Medical School, 240 Longwood Avenue, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.