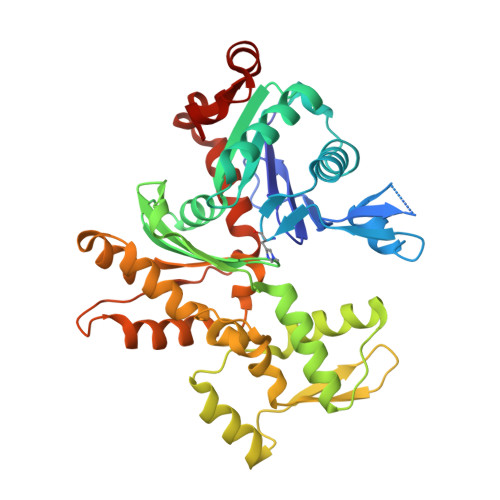
Structural basis of thymosin-beta 4/profilin exchange leading to actin filament polymerization.
Xue, B., Leyrat, C., Grimes, J.M., Robinson, R.C.(2014) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111: E4596-E4605
- PubMed: 25313062
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1412271111
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PL7, 4PL8 - PubMed Abstract:
Thymosin-β4 (Tβ4) and profilin are the two major sequestering proteins that maintain the pool of monomeric actin (G-actin) within cells of higher eukaryotes. Tβ4 prevents G-actin from joining a filament, whereas profilin:actin only supports barbed-end elongation. Here, we report two Tβ4:actin structures. The first structure shows that Tβ4 has two helices that bind at the barbed and pointed faces of G-actin, preventing the incorporation of the bound G-actin into a filament. The second structure displays a more open nucleotide binding cleft on G-actin, which is typical of profilin:actin structures, with a concomitant disruption of the Tβ4 C-terminal helix interaction. These structures, combined with biochemical assays and molecular dynamics simulations, show that the exchange of bound actin between Tβ4 and profilin involves both steric and allosteric components. The sensitivity of profilin to the conformational state of actin indicates a similar allosteric mechanism for the dissociation of profilin during filament elongation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), Biopolis, Singapore 138673; bxue@imcb.a-star.edu.sg.