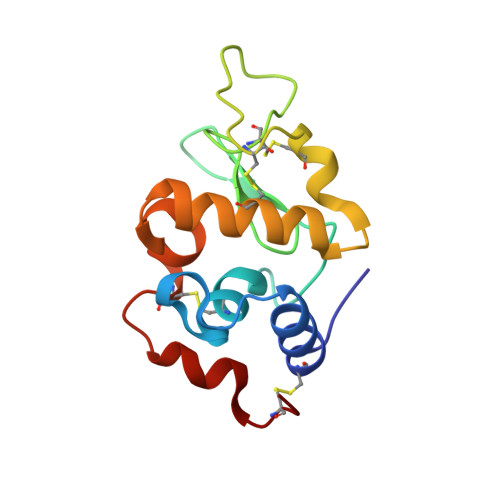
Major conformational changes in the structure of lysozyme obtained from a crystal with a very low solvent content.
Salinas-Garcia, M.C., Plaza-Garrido, M., Alba-Elena, D., Camara-Artigas, A.(2019) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 75: 687-696
- PubMed: 31702582
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X19013189
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6S7N - PubMed Abstract:
A new crystal form of lysozyme with a very low solvent content (26.35%) has been obtained in the orthorhombic space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 (with unit-cell parameters a = 30.04, b = 51.68, c = 61.53 Å). The lysozyme structure obtained from these crystals does not show the typical overall fold. Instead, major conformational changes take place in some elements of the secondary structure and in the hydrophobic core of the protein. At the end of the central α-helix (α2), Glu35 is usually buried in the catalytic site and shows an abnormally high pK a value, which is key to the activity of the enzyme. The high pK a value of this glutamate residue is favoured by the hydrophobic environment, particularly by its neighbour Trp108, which is important for structural stability and saccharide binding. In this new structure, Trp108 shows a 90° rotation of its side chain, which results in the rearrangement of the hydrophobic core. Conformational changes also result in the exposure of Glu35 to the solvent, which impairs the catalytic site by increasing the distance between Glu35 and Asp52 and lowering the pK a value of the glutamate. Altogether, this new lysozyme structure reveals major conformational changes in the hydrophobic core and catalytic site that might play a role in the folding and bactericidal function of the protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Physics, Agrifood Campus of International Excellence (ceiA3) and CIAMBITAL, University of Almería, Carretera de Sacramento s/n, 04120 Almería, Spain.