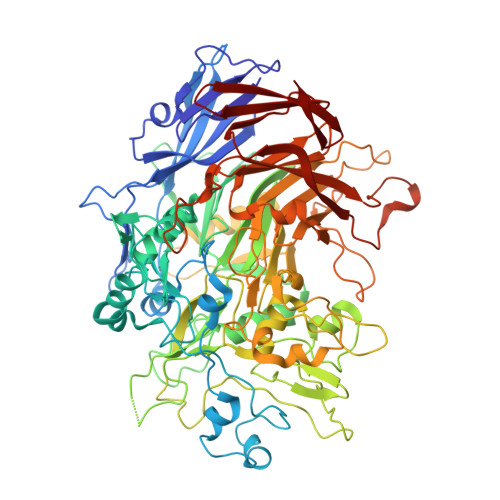
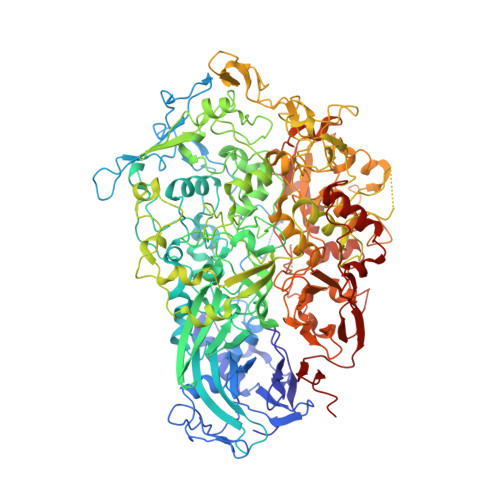
Structure and mechanism of the Nap adhesion complex from the human pathogen Mycoplasma genitalium.
Aparicio, D., Scheffer, M.P., Marcos-Silva, M., Vizarraga, D., Sprankel, L., Ratera, M., Weber, M.S., Seybert, A., Torres-Puig, S., Gonzalez-Gonzalez, L., Reitz, J., Querol, E., Pinol, J., Pich, O.Q., Fita, I., Frangakis, A.S.(2020) Nat Commun 11: 2877-2877
- PubMed: 32513917
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16511-2
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6RUT, 6S3U, 6YRK - PubMed Abstract:
Mycoplasma genitalium is a human pathogen adhering to host target epithelial cells and causing urethritis, cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease. Essential for infectivity is a transmembrane adhesion complex called Nap comprising proteins P110 and P140. Here we report the crystal structure of P140 both alone and in complex with the N-terminal domain of P110. By cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and tomography (cryo-ET) we find closed and open Nap conformations, determined at 9.8 and 15 Å, respectively. Both crystal structures and the cryo-EM structure are found in a closed conformation, where the sialic acid binding site in P110 is occluded. By contrast, the cryo-ET structure shows an open conformation, where the binding site is accessible. Structural information, in combination with functional studies, suggests a mechanism for attachment and release of M. genitalium to and from the host cell receptor, in which Nap conformations alternate to sustain motility and guarantee infectivity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Instituto de Biología Molecular de Barcelona (IBMB-CSIC) and Maria de Maeztu Unit of Excellence, Parc Científic de Barcelona, Baldiri Reixac 10, 08028, Barcelona, Spain.