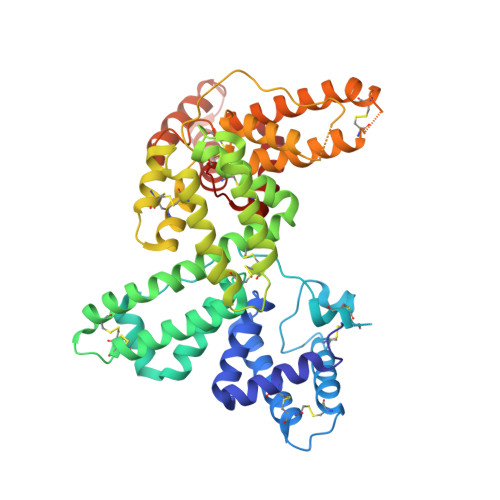
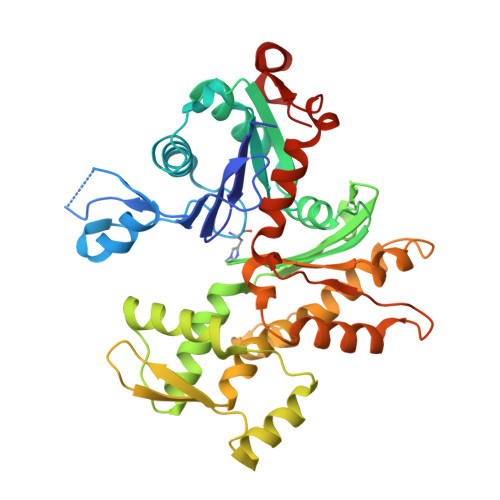
Actin-DBP: the perfect structural fit?
Verboven, C., Bogaerts, I., Waelkens, E., Rabijns, A., Van Baelen, H., Bouillon, R., De Ranter, C.(2003) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59: 263-273
- PubMed: 12554937
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444902021455
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MA9 - PubMed Abstract:
The multifunctional vitamin D binding protein (DBP) is an actin-sequestering protein present in blood. The crystal structure of the actin-DBP complex was determined at 2.4 A resolution. DBP binds to actin subdomains 1 and 3 and occludes the cleft at the interface between these subdomains. Most remarkably, DBP demonstrates an unusually large actin-binding interface, far exceeding the binding-interface areas reported for other actin-binding proteins such as profilin, DNase I and gelsolin. The fast-growing side of actin monomers is blocked completely through a perfect structural fit with DBP, demonstrating how DBP effectively interferes with actin-filament formation. It establishes DBP as the hitherto best actin-sequestering protein and highlights its key role in suppressing and preventing extracellular actin polymerization.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratorium voor Analytische Chemie en Medicinale Fysicochemie, Faculteit Farmaceutische Wetenschappen, K. U. Leuven, Belgium.