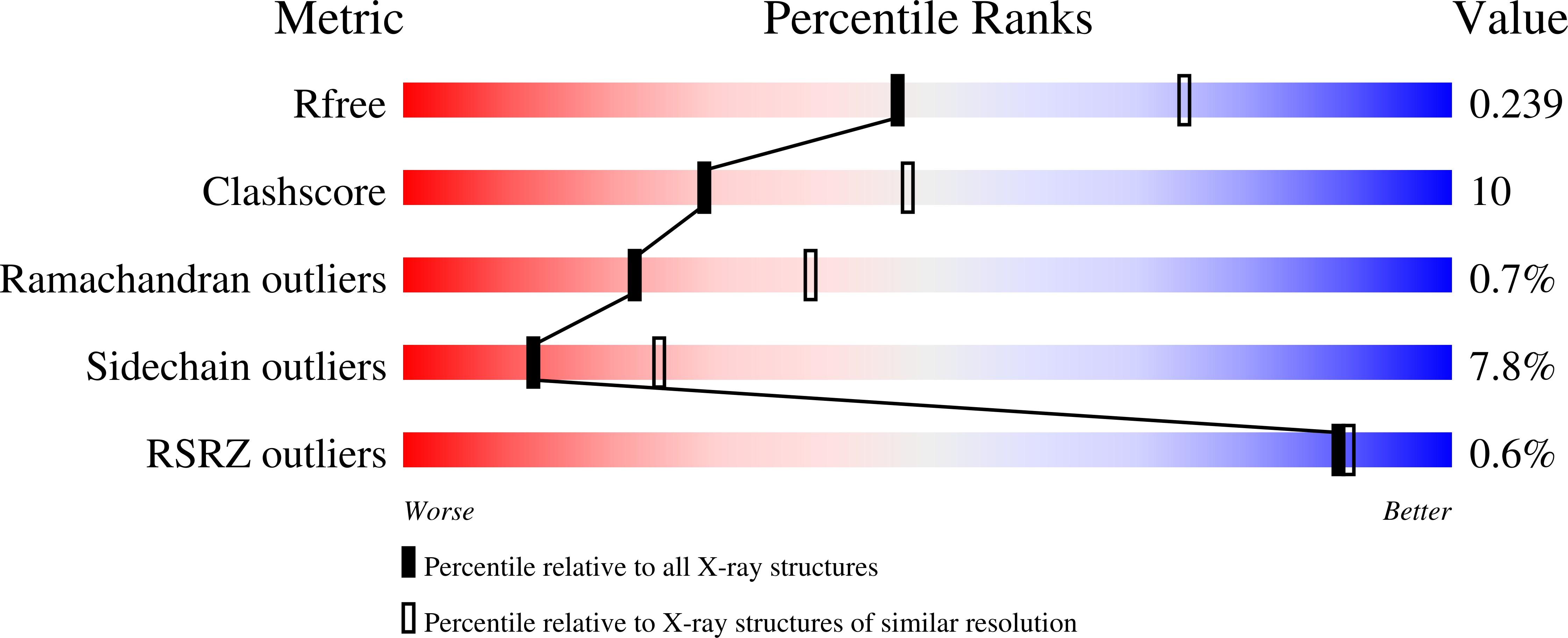
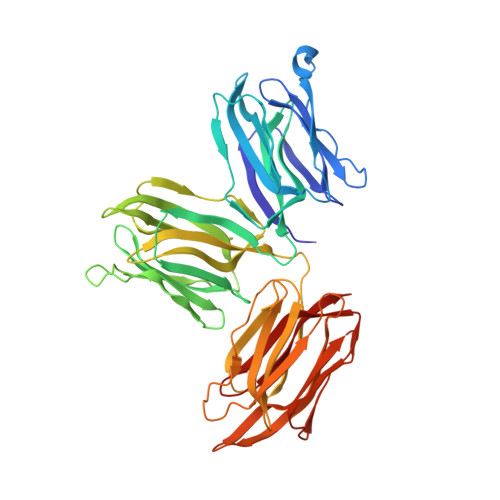
The first crystal structure of a mimosoideae lectin reveals a novel quaternary arrangement of a widespread domain.
Gallego Del Sol, F., Nagano, C., Cavada, B.S., Calvete, J.J.(2005) J Mol Biol 353: 574-583
- PubMed: 16185708
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.08.055
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ZGR, 1ZGS - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structures of the apo and mannose-bound Parkia platycephala seed lectin represent the first structure of a Mimosoideae lectin and a novel circular arrangement of beta-prism domains, and highlight the adaptability of the beta-prism fold as a building block in the evolution of plant lectins. The P.platycephala lectin is a dimer both in solution and in the crystals. Mannose binding to each of the three homologous carbohydrate-recognition domains of the lectin occurs through different modes, and restrains the flexibility of surface-exposed loops and residues involved in carbohydrate recognition. The planar array of carbohydrate-binding sites on the rim of the toroid-shaped structure of the P.platycephala lectin dimer immediately suggests a mechanism to promote multivalent interactions leading to cross-linking of carbohydrate ligands as part of the host strategy against phytopredators and pathogens. The cyclic structure of the P.platycephala lectin points to the convergent evolution of a structural principle for the construction of lectins involved in host defense or in attacking other organisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia, CSIC, E-46010 Valencia, Spain.