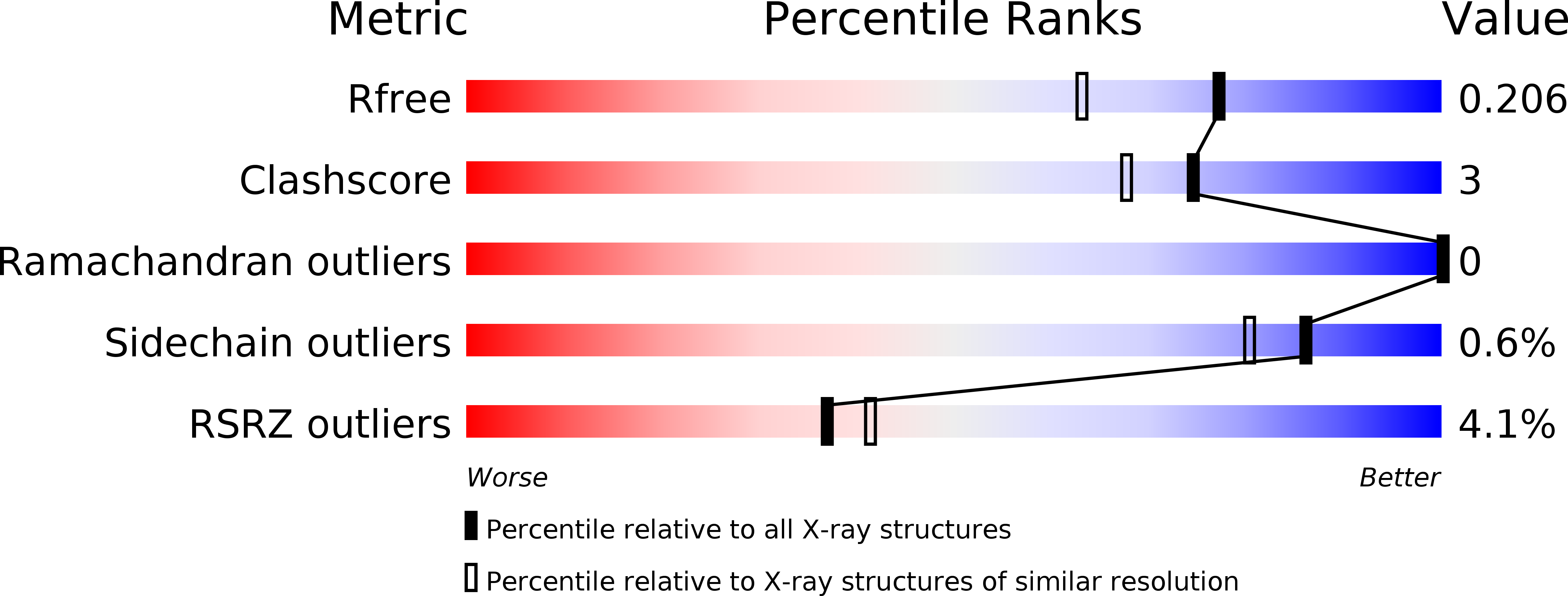
X-ray crystal structure of putative transcription regulator lmo2088 from Listeria monocytogenes.
Samad, A., Li, Y., Zhang, C., Chen, F., Zeng, W., Fan, X., Jin, T.(2019) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 520: 434-440
- PubMed: 31607473
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.033
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ZTC - PubMed Abstract:
Listeria monocytogenes is a gram-positive food borne pathogen. The lmo2088 belongs to the TetR family of transcriptional regulators from L. monocytogenes. These transcriptional factors regulate multidrug resistance transporters in L. monocytogenes. Here, we report native protein crystal structure of lmo2088 at a resolution of 1.7 Å. Lmo2088 comprises of an N-terminal DNA binding domain and a variable C-terminal effector binding domain. Furthermore, we identified specific consensus sequences selected by systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment in vitro. The specific binding of lmo2088 with DNA consensus sequence was validated by electrophoretic mobility shift assay, fluorescence polarization and isothermal titration calorimetry. We speculate that the structure of lmo2088 might provide an insight into the regulatory function of lmo2088 of L. monocytogenes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China; Division of Molecular Medicine, Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale, CAS Key Laboratory of Innate Immunity and Chronic Disease, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, China.