Novel Tricyclic Pyroglutamide Derivatives as Potent ROR gamma t Inverse Agonists Identified using a Virtual Screening Approach.
Liu, Q., Batt, D.G., Weigelt, C.A., Yip, S., Wu, D.R., Ruzanov, M., Sack, J.S., Wang, J., Yarde, M., Li, S., Shuster, D.J., Xie, J.H., Sherry, T., Obermeier, M.T., Fura, A., Stefanski, K., Cornelius, G., Khandelwal, P., Tino, J.A., Macor, J.E., Salter-Cid, L., Denton, R., Zhao, Q., Dhar, T.G.M.(2020) ACS Med Chem Lett 11: 2510-2518
- PubMed: 33335675
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00496
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
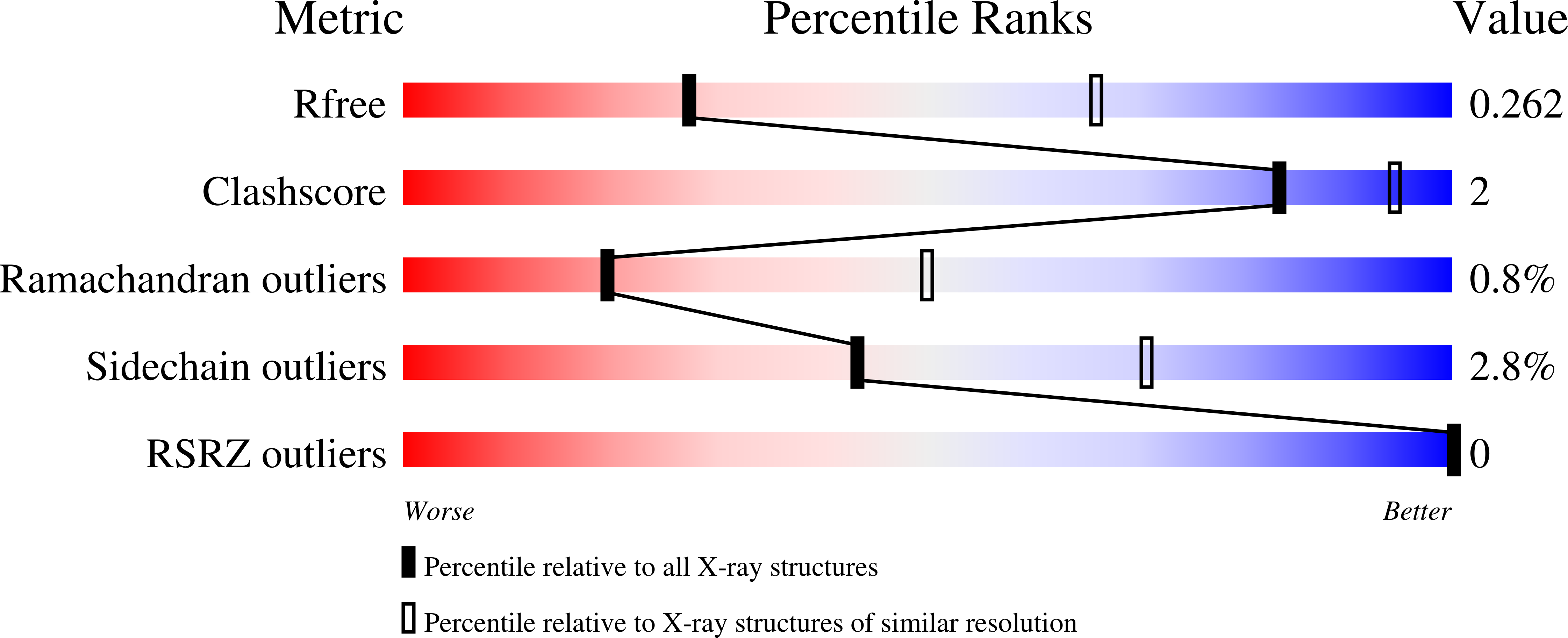
7JYM - PubMed Abstract:
Employing a virtual screening approach, we identified the pyroglutamide moiety as a nonacid replacement for the cyclohexanecarboxylic acid group which, when coupled to our previously reported conformationally locked tricyclic core, provided potent and selective RORγt inverse agonists. Structure-activity relationship optimization of the pyroglutamide moiety led to the identification of compound 18 as a potent and selective RORγt inverse agonist, albeit with poor aqueous solubility. We took advantage of the tertiary carbinol group in 18 to synthesize a phosphate prodrug, which provided good solubility, excellent exposures in mouse PK studies, and significant efficacy in a mouse model of psoriasis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research and Early Development, Bristol Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, New Jersey 08540-4000, United States.