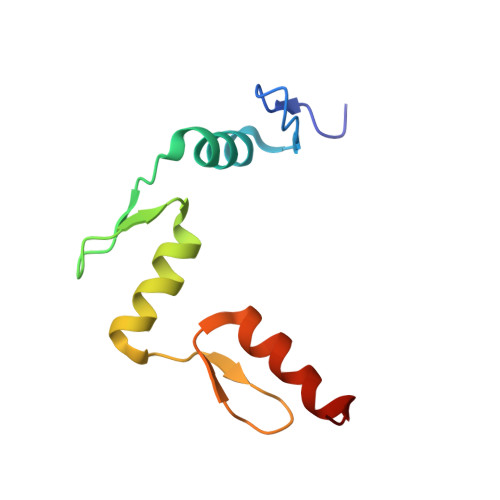
Beyond the "recognition code": structures of two Cys2His2 zinc finger/TATA box complexes.
Wolfe, S.A., Grant, R.A., Elrod-Erickson, M., Pabo, C.O.(2001) Structure 9: 717-723
- PubMed: 11587646
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00632-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1G2D, 1G2F - PubMed Abstract:
Several methods have been developed for creating Cys2His2 zinc finger proteins that recognize novel DNA sequences, and these proteins may have important applications in biological research and gene therapy. In spite of this progress with design/selection methodology, fundamental questions remain about the principles that govern DNA recognition. One hypothesis suggests that recognition can be described by a simple set of rules--essentially a "recognition code"--but careful assessment of this proposal has been difficult because there have been few structural studies of selected zinc finger proteins. We report the high-resolution cocrystal structures of two zinc finger proteins that had been selected (as variants of Zif268) to recognize a eukaryotic TATA box sequence. The overall docking arrangement of the fingers within the major groove of the DNA is similar to that observed in the Zif268 complex. Nevertheless, comparison of Zif268 and the selected variants reveal significant differences in the pattern of side chain-base interactions. The new structures also reveal side chain-side chain interactions (both within and between fingers) that are important in stabilizing the protein-DNA interface and appear to play substantial roles in recognition. These new structures highlight the surprising complexity of zinc finger-DNA interactions. The diversity of interactions observed at the protein-DNA interface, which is especially striking for proteins that were all derived from Zif268, challenges fundamental concepts about zinc finger-DNA recognition and underscores the difficulty in developing any meaningful recognition code.
- Department of Biology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: