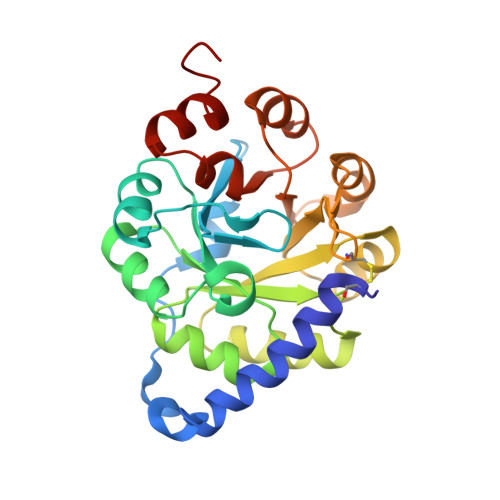
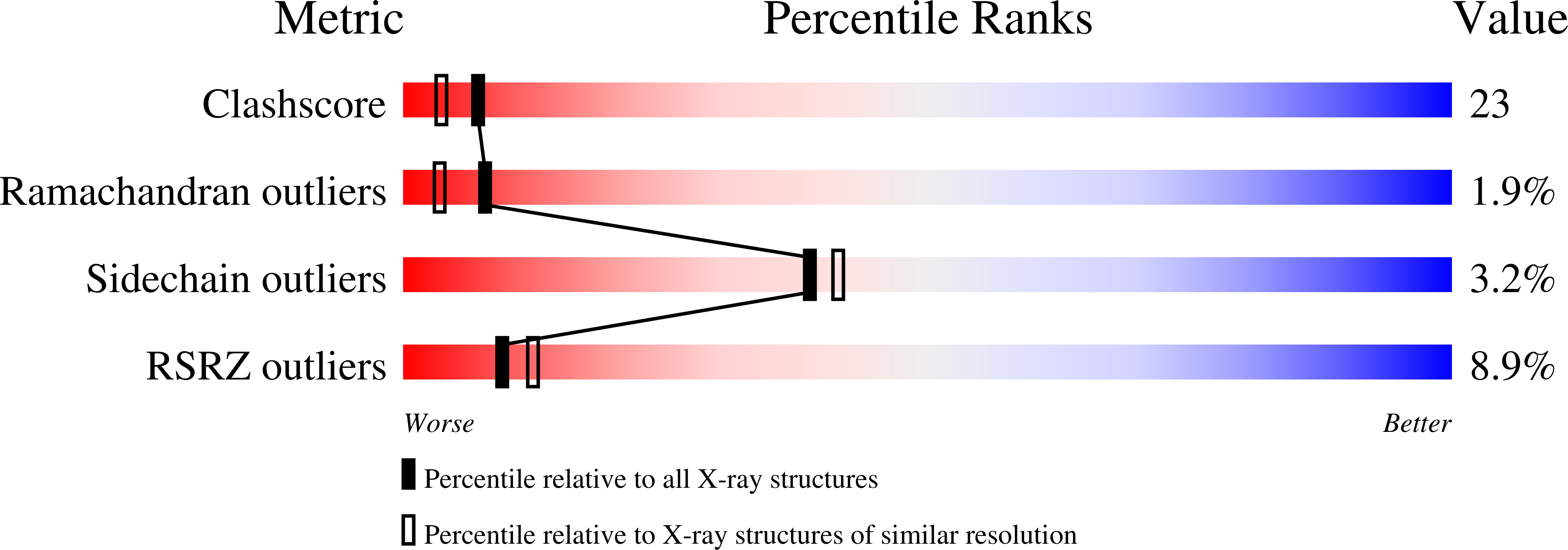Stabilization of a (betaalpha)8-barrel protein by an engineered disulfide bridge.
Ivens, A., Mayans, O., Szadkowski, H., Jurgens, C., Wilmanns, M., Kirschner, K.(2002) Eur J Biochem 269: 1145-1153
- PubMed: 11856350
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02745.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JCM - PubMed Abstract:
The aim of this study was to increase the stability of the thermolabile (betaalpha)8-barrel enzyme indoleglycerol phosphate synthase from Escherichia coli by the introduction of disulfide bridges. For the design of such variants, we selected two out of 12 candidates, in which newly introduced cysteines potentially form optimal disulfide bonds. These variants avoid short-range connections, substitutions near catalytic residues, and crosslinks between the new and the three parental cysteines. The variant linking residues 3 and 189 fastens the N-terminus to the (betaalpha)8-barrel. The rate of thermal inactivation at 50 degrees C of this variant with a closed disulfide bridge is 65-fold slower than that of the reference dithiol form, but only 13-fold slower than that of the parental protein. The near-ultraviolet CD spectrum, the reactivity of parental buried cysteines with Ellman's reagent as well as the decreased turnover number indicate that the protein structure is rigidified. To confirm these data, we have solved the X-ray structure to 2.1-A resolution. The second variant was designed to crosslink the terminal modules betaalpha1 and betaalpha8. However, not even the dithiol form acquired the native fold, possibly because one of the targeted residues is solvent-inaccessible in the parental protein.
Organizational Affiliation:
Universität zu Köln, Institut für Biochemie, Köln, Germany. andreas.ivens@uni-koeln.de