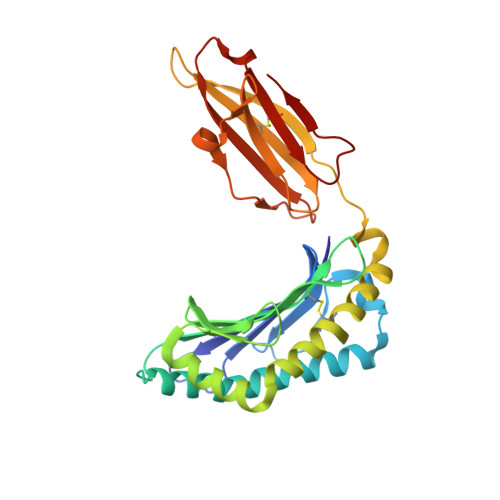
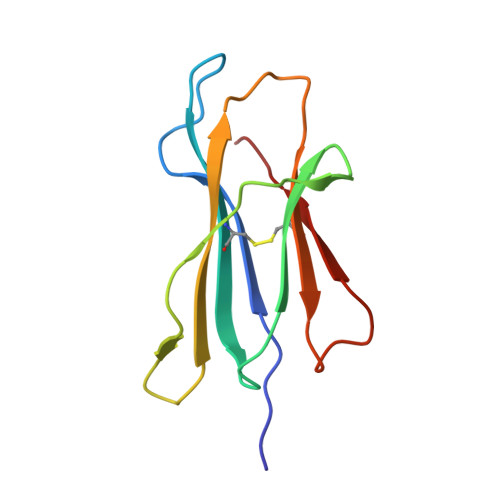
Structure of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-Cw4, a ligand for the KIR2D natural killer cell inhibitory receptor
Fan, Q.R., Wiley, D.C.(1999) J Exp Medicine 190: 113-123
- PubMed: 10429675
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.190.1.113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QQD - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the human class I major histocompatibility complex molecule, human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-Cw4, the ligand for a natural killer (NK) cell inhibitory receptor, has been determined, complexed with a nonameric consensus peptide (QYDDAVYKL). Relative to HLA-A2, the peptide binding groove is widened around the COOH terminus of the alpha 1 helix, which contains residues that determine the specificity of HLA-Cw4 for the inhibitory NK receptor, KIR2D. The structure reveals an unusual pattern of internal hydrogen bonding among peptide residues. The peptide is anchored in four specificity pockets in the cleft and secured by extensive hydrogen bonds between the peptide main chain and the cleft. The surface of HLA-Cw4 has electrostatic complementarity to the surface of the NK cell inhibitory receptor KIR2D.
- Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: