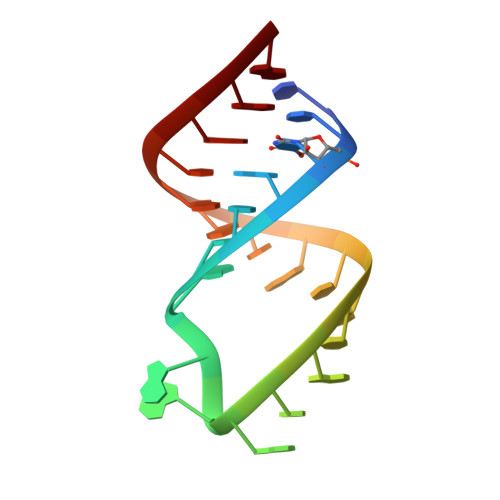
Targeting the dimerization initiation site of HIV-1 RNA with aminoglycosides: from crystal to cell.
Ennifar, E., Paillart, J.C., Bodlenner, A., Walter, P., Weibel, J.-M., Aubertin, A.-M., Pale, P., Dumas, P., Marquet, R.(2006) Nucleic Acids Res 34: 2328-2339
- PubMed: 16679451
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl317
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FCX, 2FCY, 2FCZ, 2FD0 - PubMed Abstract:
The kissing-loop complex that initiates dimerization of genomic RNA is crucial for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) replication. We showed that owing to its strong similitude with the bacterial ribosomal A site it can be targeted by aminoglycosides. Here, we present its crystal structure in complex with neamine, ribostamycin, neomycin and lividomycin. These structures explain the specificity for 4,5-disubstituted 2-deoxystreptamine (DOS) derivatives and for subtype A and subtype F kissing-loop complexes, and provide a strong basis for rational drug design. As a consequence of the different topologies of the kissing-loop complex and the A site, these aminoglycosides establish more contacts with HIV-1 RNA than with 16S RNA. Together with biochemical experiments, they showed that while rings I, II and III confer binding specificity, rings IV and V are important for affinity. Binding of neomycin, paromomycin and lividomycin strongly stabilized the kissing-loop complex by bridging the two HIV-1 RNA molecules. Furthermore, in situ footprinting showed that the dimerization initiation site (DIS) of HIV-1 genomic RNA could be targeted by these aminoglycosides in infected cells and virions, demonstrating its accessibility.
- UPR 9002 du CNRS conventionnée à l'Université Louis Pasteur, IBMC 15 rue René Descartes, 67084, Strasbourg cedex, France.
Organizational Affiliation: