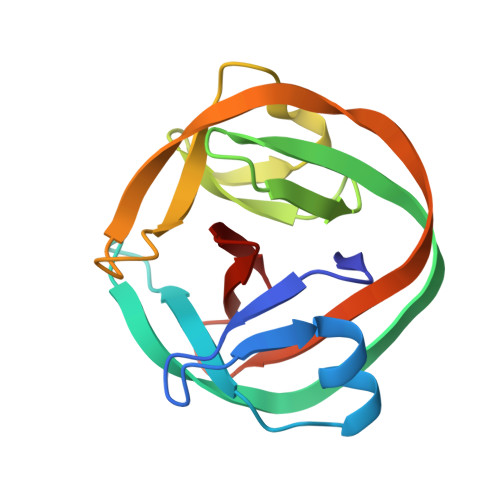
Crystallographic and mutational studies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis recA mini-inteins suggest a pivotal role for a highly conserved aspartate residue.
Van Roey, P., Pereira, B., Li, Z., Hiraga, K., Belfort, M., Derbyshire, V.(2007) J Mol Biology 367: 162-173
- PubMed: 17254599
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.050
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2IMZ, 2IN0, 2IN8, 2IN9 - PubMed Abstract:
The 440 amino acid Mtu recA intein consists of independent protein-splicing and endonuclease domains. Previously, removal of the central endonuclease domain of the intein, and selection for function, generated a 168 residue mini-intein, DeltaI-SM, that had splicing activity similar to that of the full-length, wild-type protein. A D422G mutation (DeltaI-CM) increased C-terminal cleavage activity. Using the DeltaI-SM mini-intein structure (presented here) as a guide, we previously generated a highly active 139 residue mini-intein, DeltaDeltaI(hh)-SM, by replacing 36 amino acid residues in the residual endonuclease loop with a seven-residue beta-turn from the autoprocessing domain of Hedgehog protein. The three-dimensional structures of DeltaI-SM, DeltaDeltaI(hh)-SM, and two variants, DeltaDeltaI(hh)-CM and DeltaDeltaI(hh), have been determined to evaluate the effects of the minimization on intein integrity and to investigate the structural and functional consequences of the D422G mutation. These structural studies show that Asp422 is capable of interacting with both the N and C termini. These interactions are lacking in the CM variant, but are replaced by contacts with water molecules. Accordingly, additional mutagenesis of residue 422, combined with mutations that isolate N-terminal and C-terminal cleavage, showed that the side-chain of Asp422 plays a role in both N and C-terminal cleavage, thereby suggesting that this highly conserved residue regulates the balance between the two reactions.
- Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health, Center for Medical Sciences, 150 New Scotland Avenue, Albany, NY 12208, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: