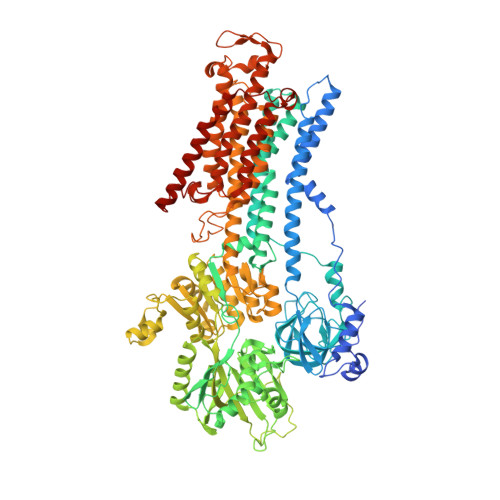
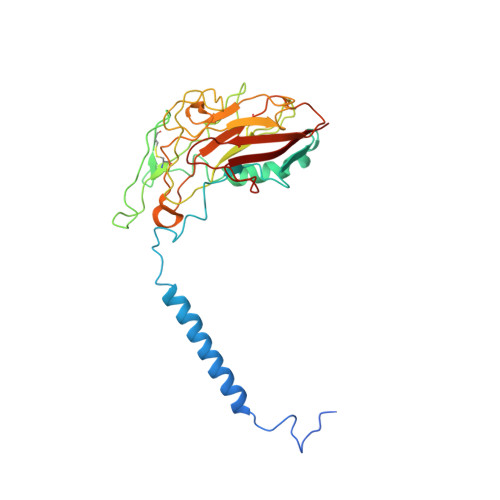
Crystal structure of Na+, K(+)-ATPase in the Na(+)-bound state.
Nyblom, M., Poulsen, H., Gourdon, P., Reinhard, L., Andersson, M., Lindahl, E., Fedosova, N., Nissen, P.(2013) Science 342: 123-127
- PubMed: 24051246
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1243352
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4HQJ - PubMed Abstract:
The Na(+), K(+)-adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) maintains the electrochemical gradients of Na(+) and K(+) across the plasma membrane--a prerequisite for electrical excitability and secondary transport. Hitherto, structural information has been limited to K(+)-bound or ouabain-blocked forms. We present the crystal structure of a Na(+)-bound Na(+), K(+)-ATPase as determined at 4.3 Å resolution. Compared with the K(+)-bound form, large conformational changes are observed in the α subunit whereas the β and γ subunit structures are maintained. The locations of the three Na(+) sites are indicated with the unique site III at the recently suggested IIIb, as further supported by electrophysiological studies on leak currents. Extracellular release of the third Na(+) from IIIb through IIIa, followed by exchange of Na(+) for K(+) at sites I and II, is suggested.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Membrane Pumps in Cells and Disease-PUMPkin, Danish National Research Foundation, DK-8000 Aarhus, Denmark.