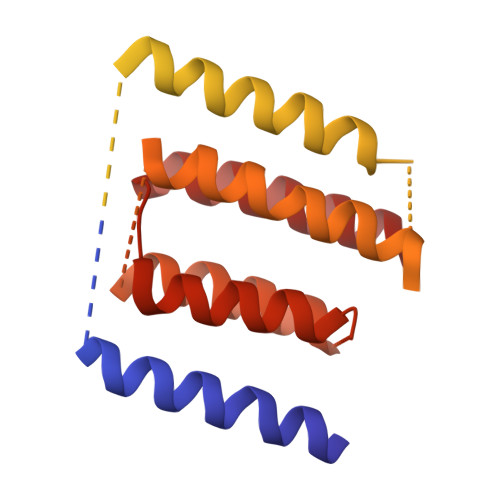
A Structural Model of the Active Ribosome-Bound Membrane Protein Insertase Yidc.
Wickles, S., Singharoy, A., Andreani, J., Seemayer, S., Bischoff, L., Berninghausen, O., Soeding, J., Schulten, K., Van Der Sluis, E.O., Beckmann, R.(2014) Elife 3: 3035
- PubMed: 25012291
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.03035
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4UTQ - PubMed Abstract:
The integration of most membrane proteins into the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria occurs co-translationally. The universally conserved YidC protein mediates this process either individually as a membrane protein insertase, or in concert with the SecY complex. Here, we present a structural model of YidC based on evolutionary co-variation analysis, lipid-versus-protein-exposure and molecular dynamics simulations. The model suggests a distinctive arrangement of the conserved five transmembrane domains and a helical hairpin between transmembrane segment 2 (TM2) and TM3 on the cytoplasmic membrane surface. The model was used for docking into a cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of a translating YidC-ribosome complex carrying the YidC substrate FOc. This structure reveals how a single copy of YidC interacts with the ribosome at the ribosomal tunnel exit and identifies a site for membrane protein insertion at the YidC protein-lipid interface. Together, these data suggest a mechanism for the co-translational mode of YidC-mediated membrane protein insertion.
- Gene Center Munich, Department of Biochemistry, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Munich, Germany Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich, Department of Biochemistry, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Munich, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: