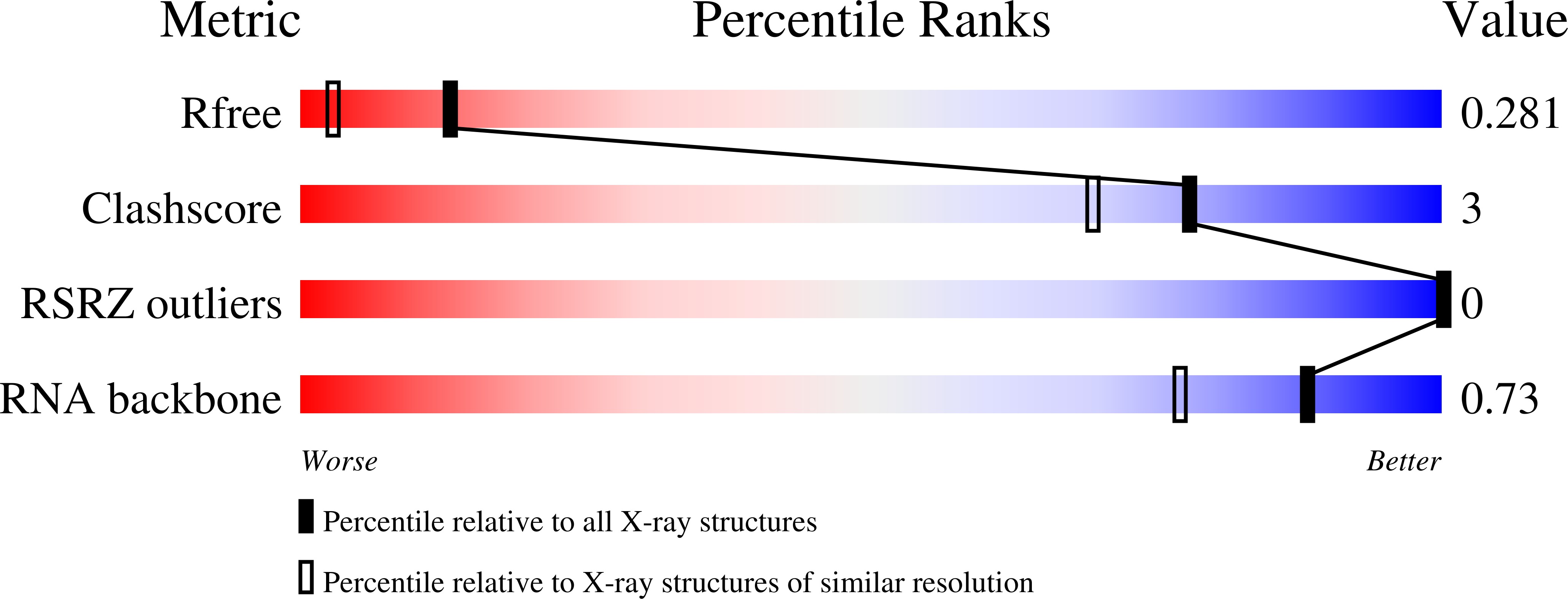Crystallographic observation of nonenzymatic RNA primer extension.
Zhang, W., Walton, T., Li, L., Szostak, J.W.(2018) Elife 7
- PubMed: 29851379
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.36422
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6C8D, 6C8E, 6C8I, 6C8J, 6C8K, 6C8L, 6C8M, 6C8N, 6C8O, 6CAB - PubMed Abstract:
The importance of genome replication has inspired detailed crystallographic studies of enzymatic DNA/RNA polymerization. In contrast, the mechanism of nonenzymatic polymerization is less well understood, despite its critical role in the origin of life. Here we report the direct observation of nonenzymatic RNA primer extension through time-resolved crystallography. We soaked crystals of an RNA primer-template-dGMP complex with guanosine-5'-phosphoro-2-aminoimidazolide for increasing times. At early times we see the activated ribonucleotides bound to the template, followed by formation of the imidazolium-bridged dinucleotide intermediate. At later times, we see a new phosphodiester bond forming between the primer and the incoming nucleotide. The intermediate is pre-organized because of the constraints of base-pairing with the template and hydrogen bonding between the imidazole amino group and both flanking phosphates. Our results provide atomic-resolution insight into the mechanism of nonenzymatic primer extension, and set the stage for further structural dissection and optimization of the RNA copying process.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, United States.