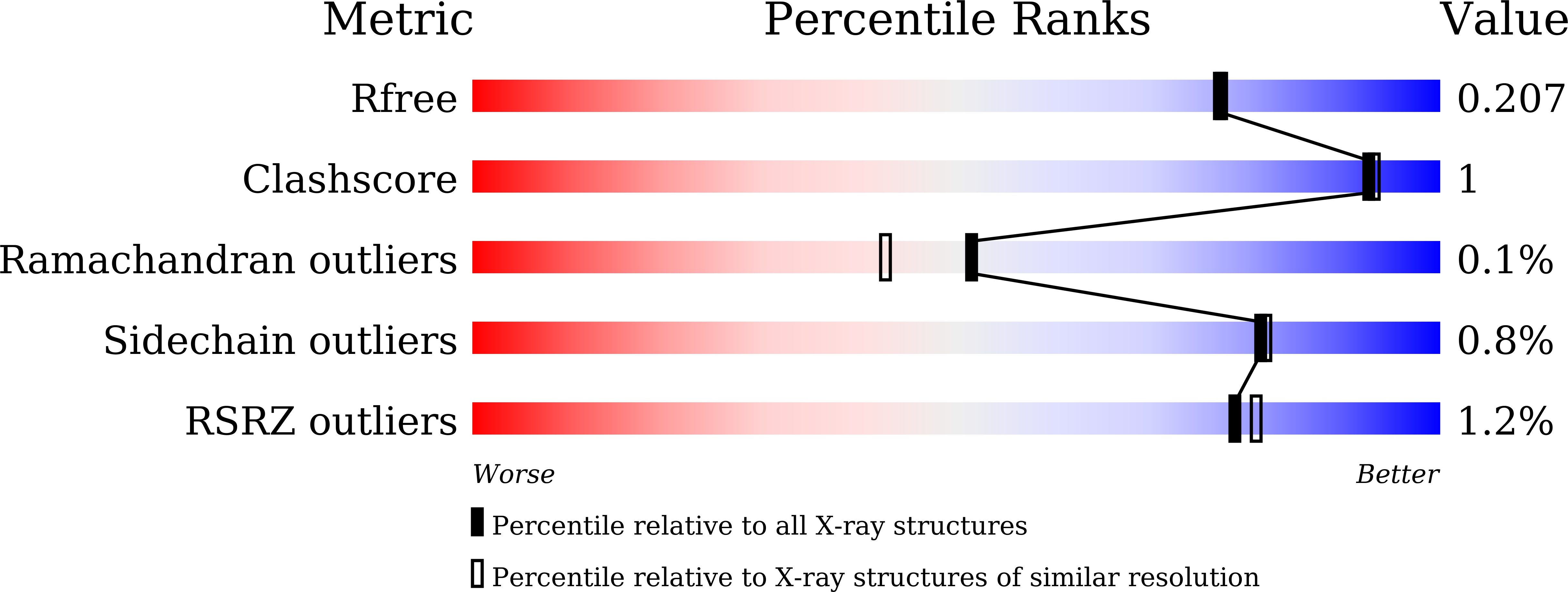
Structure-function analysis of silkworm sucrose hydrolase uncovers the mechanism of substrate specificity in GH13 subfamily 17exo-alpha-glucosidases.
Miyazaki, T., Park, E.Y.(2020) J Biol Chem 295: 8784-8797
- PubMed: 32381508
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.013595
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6LGA, 6LGB, 6LGC, 6LGD, 6LGE, 6LGF, 6LGG, 6LGH, 6LGI - PubMed Abstract:
The domestic silkworm Bombyx mori expresses two sucrose-hydrolyzing enzymes, BmSUH and BmSUC1, belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 13 subfamily 17 (GH13_17) and GH32, respectively. BmSUH has little activity on maltooligosaccharides, whereas other insect GH13_17 α-glucosidases are active on sucrose and maltooligosaccharides. Little is currently known about the structural mechanisms and substrate specificity of GH13_17 enzymes. In this study, we examined the crystal structures of BmSUH without ligands; in complexes with substrates, products, and inhibitors; and complexed with its covalent intermediate at 1.60-1.85 Å resolutions. These structures revealed that the conformations of amino acid residues around subsite -1 are notably different at each step of the hydrolytic reaction. Such changes have not been previously reported among GH13 enzymes, including exo - and endo -acting hydrolases, such as α-glucosidases and α-amylases. Amino acid residues at subsite +1 are not conserved in BmSUH and other GH13_17 α-glucosidases, but subsite -1 residues are absolutely conserved. Substitutions in three subsite +1 residues, Gln 191 , Tyr 251 , and Glu 440 , decreased sucrose hydrolysis and increased maltase activity of BmSUH, indicating that these residues are key for determining its substrate specificity. These results provide detailed insights into structure-function relationships in GH13 enzymes and into the molecular evolution of insect GH13_17 α-glucosidases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Green Chemistry Research Division, Research Institute of Green Science and Technology, Shizuoka University, Shizuoka, Japan. Electronic address: miyazaki.takatsugu@shizuoka.ac.jp.