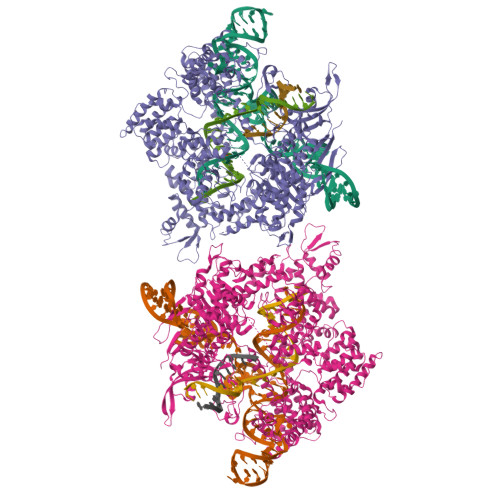
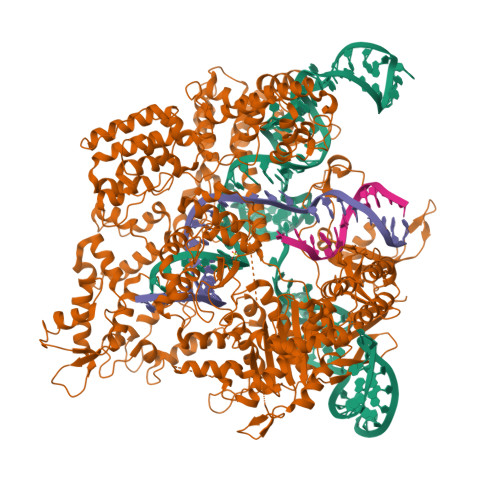
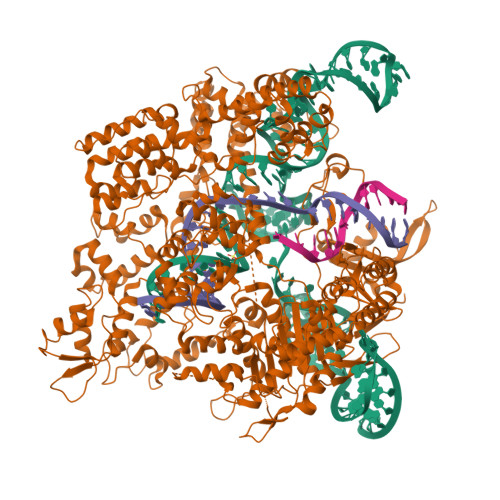
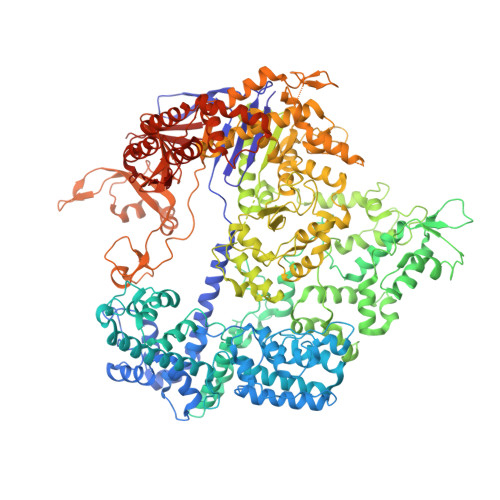
Trans-nuclease activity of Cas9 activated by DNA or RNA target binding.
Chen, J., Chen, Y., Huang, L., Lin, X., Chen, H., Xiang, W., Liu, L.(2024) Nat Biotechnol
- PubMed: 38811761
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02255-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8KAG, 8KAH, 8KAI, 8KAJ, 8KAK, 8KAL, 8KAM - PubMed Abstract:
Type V and type VI CRISPR-Cas systems have been shown to cleave nonspecific single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) in trans, but this has not been observed in type II CRISPR-Cas systems using single guide RNA. We show here that the type II CRISPR-Cas9 systems directed by CRISPR RNA and trans-activating CRISPR RNA dual RNAs show RuvC domain-dependent trans-cleavage activity for both ssDNA and ssRNA substrates. Cas9 possesses sequence preferences for trans-cleavage substrates, preferring to cleave T- or C-rich ssDNA substrates. We find that the trans-cleavage activity of Cas9 can be activated by target ssDNA, double-stranded DNA and ssRNA. The crystal structure of Cas9 in complex with guide RNA and target RNA provides a structural basis for the binding of target RNA to activate Cas9. Based on the trans-cleavage activity of Cas9 and nucleic acid amplification technology, we develop the nucleic acid detection platforms DNA-activated Cas9 detection and RNA-activated Cas9 detection, which are capable of detecting DNA and RNA samples with high sensitivity and specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, School of Life Sciences, Faculty of Medicine and Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China.