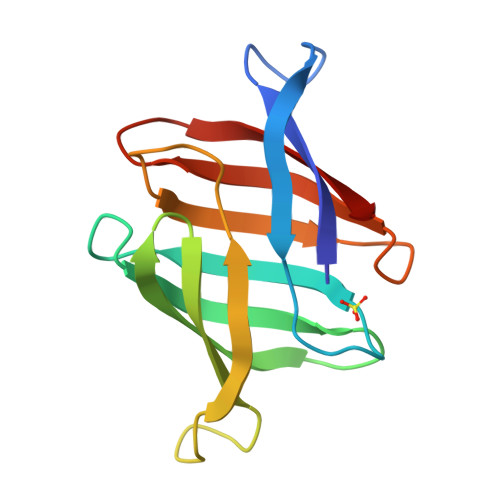
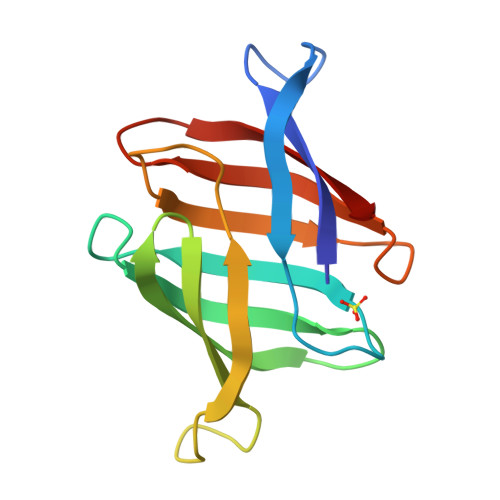
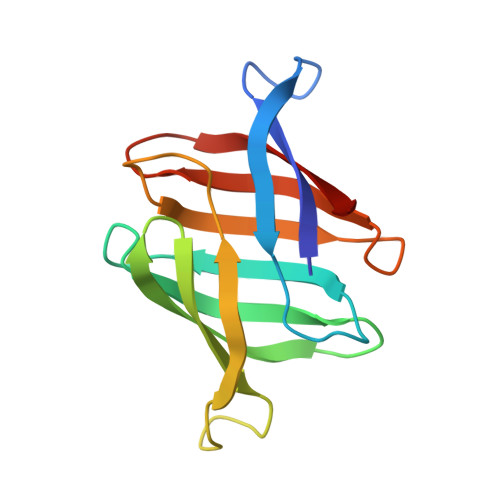
Structural basis of the anti-HIV activity of the cyanobacterial Oscillatoria Agardhii agglutinin.
Koharudin, L.M., Gronenborn, A.M.(2011) Structure 19: 1170-1181
- PubMed: 21827952
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.05.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3S5V, 3S5X, 3S60 - PubMed Abstract:
The cyanobacterial Oscillatory Agardhii agglutinin (OAA) is a recently discovered HIV-inactivating lectin that interacts with high-mannose sugars. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) binding studies between OAA and α3,α6-mannopentaose (Manα(1-3)[Manα(1-3)[Manα(1-6)]Manα(1-6)]Man), the branched core unit of Man-9, revealed two binding sites at opposite ends of the protein, exhibiting essentially identical affinities. Atomic details of the specific protein-sugar contacts in the recognition loops of OAA were delineated in the high-resolution crystal structures of free and glycan-complexed protein. No major changes in the overall protein structure are induced by carbohydrate binding, with essentially identical apo- and sugar-bound conformations in binding site 1. A single peptide bond flip at W77-G78 is seen in binding site 2. Our combined NMR and crystallographic results provide structural insights into the mechanism by which OAA specifically recognizes the branched Man-9 core, distinctly different from the recognition of the D1 and D3 arms at the nonreducing end of high-mannose carbohydrates by other antiviral lectins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Biomedical Science Tower 3, Pittsburgh, PA 15260, USA.