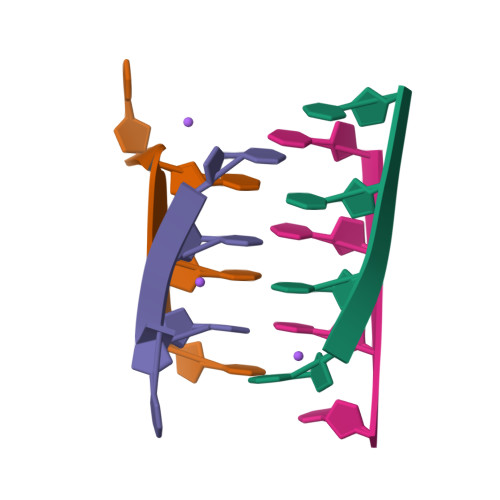
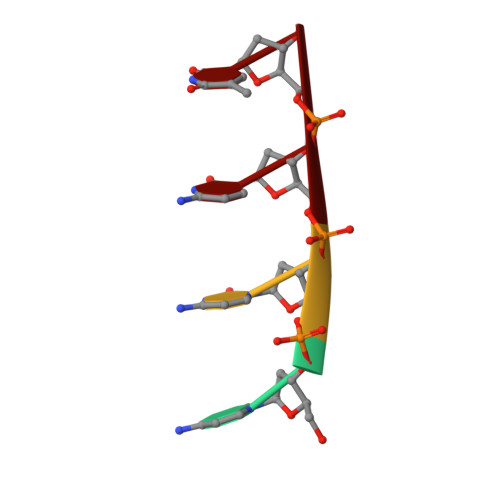
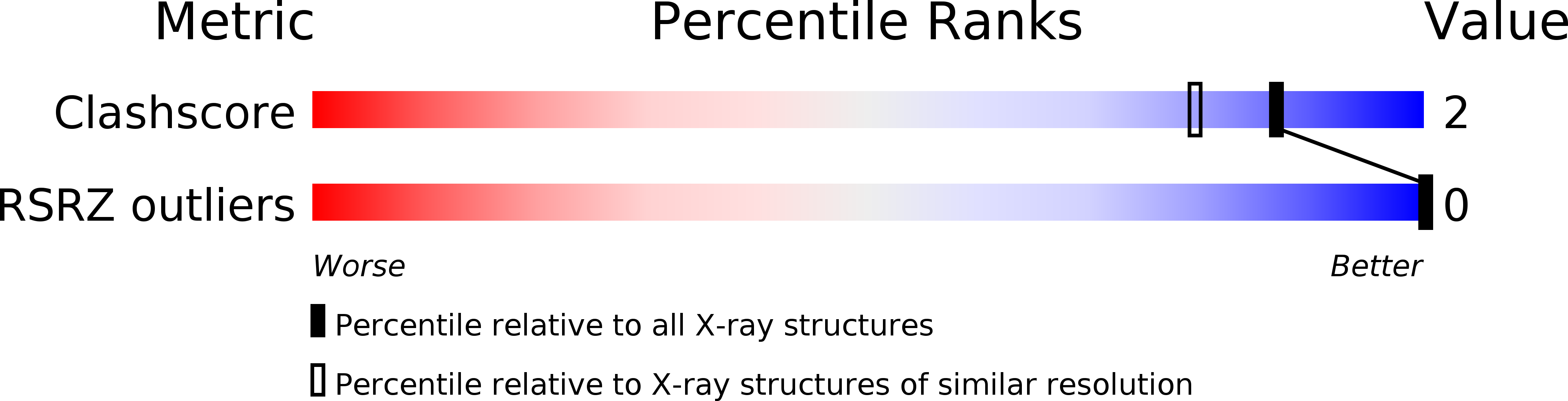Crystal structure of intercalated four-stranded d(C3T) at 1.4 angstroms resolution.
Kang, C.H., Berger, I., Lockshin, C., Ratliff, R., Moyzis, R., Rich, A.(1994) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91: 11636-11640
- PubMed: 7972115
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.24.11636
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
191D - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of d(C3T), solved at 1.4 A resolution, reveals that the molecule forms a four-stranded intercalated complex. It consists of two parallel-stranded duplexes, each of which is held together by cytosine-protonated cytosine base pairs. The two duplexes are intercalated with each other and have opposite strand orientation. The molecule has a flat, lath-like appearance, and the covalently bonded cytosines have a slow right-handed twist of 17.1 degrees. However, there is considerable asymmetry. On one of the flat sides, the phosphate groups are rotated away from the center of the molecule. They are held in this orientation by bridging water molecules that bind the NH of cytosine and a phosphate group of an opposite chain. There is also considerable microheterogeneity in the structure. The cytosine hemiprotonation occurs even at pH 7 where stable crystals form.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge 02139.