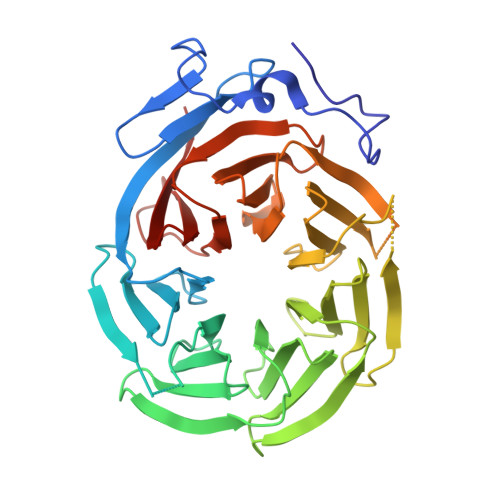
Structure of the C-terminal domain of Tup1, a corepressor of transcription in yeast.
Sprague, E.R., Redd, M.J., Johnson, A.D., Wolberger, C.(2000) EMBO J 19: 3016-3027
- PubMed: 10856245
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.12.3016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ERJ - PubMed Abstract:
The Tup1-Ssn6 corepressor complex regulates the expression of several sets of genes, including genes that specify mating type in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Repression of mating-type genes occurs when Tup1-Ssn6 is brought to the DNA by the Matalpha2 DNA-binding protein and assembled upstream of a- and haploid-specific genes. We have determined the 2.3 A X-ray crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of Tup1 (accesion No. 1ERJ), a 43 kDa fragment that contains seven copies of the WD40 sequence motif and binds to the Matalpha2 protein. Moreover, this portion of the protein can partially substitute for full-length Tup1 in bringing about transcriptional repression. The structure reveals a seven-bladed beta propeller with an N-terminal subdomain that is anchored to the side of the propeller and extends the beta sheet of one of the blades. Point mutations in Tup1 that specifically affect the Tup1-Matalpha2 interaction cluster on one surface of the propeller. We identified regions of Tup1 that are conserved among the fungal Tup1 homologs and may be important in protein-protein interactions with additional components of the Tup1-mediated repression pathways.
- Department of Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry and Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: