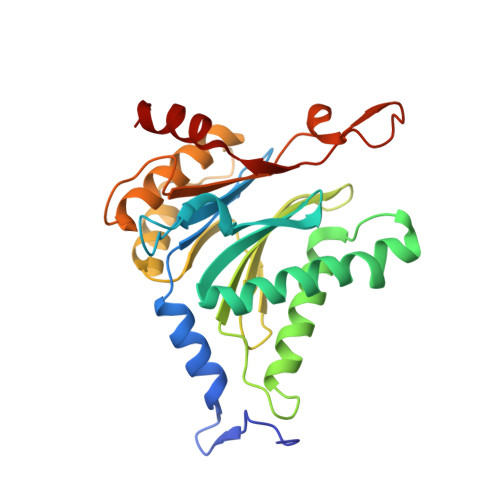
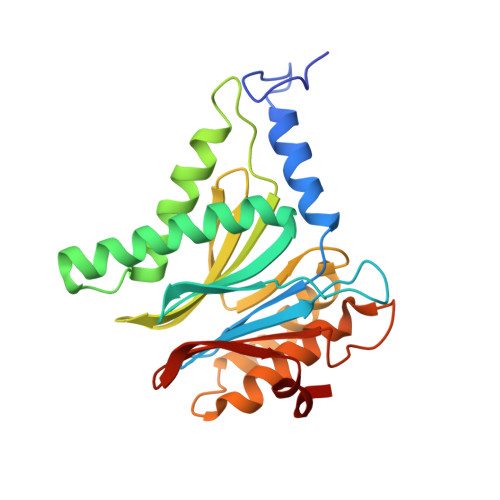
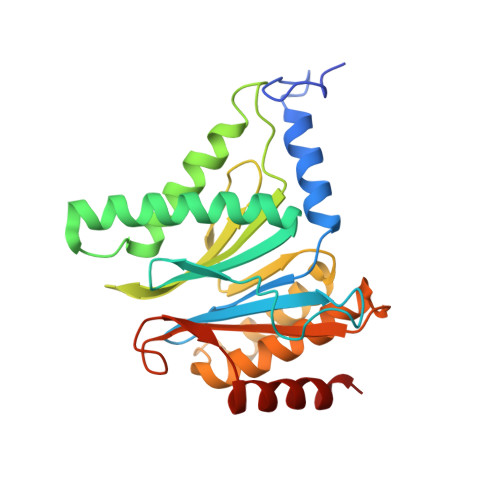
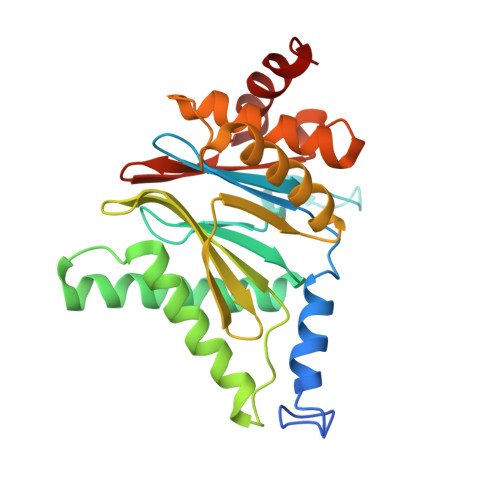
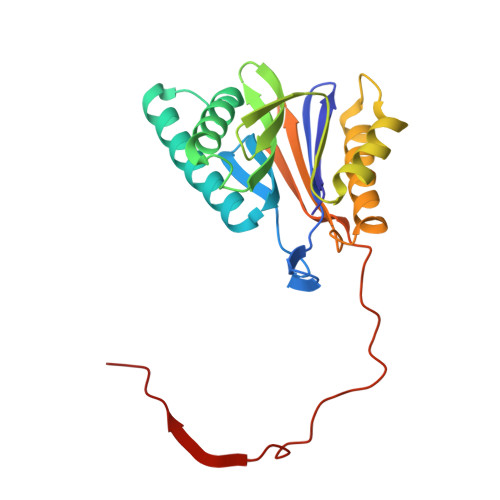
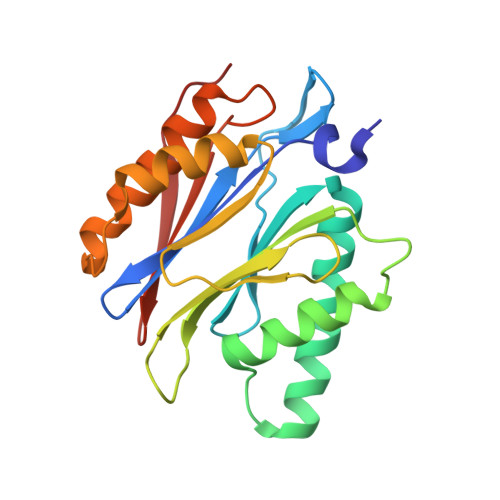
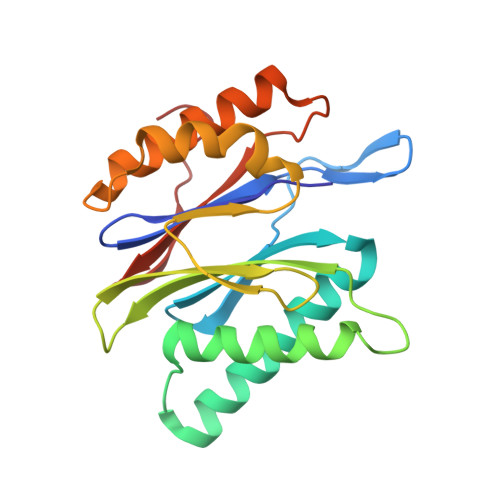
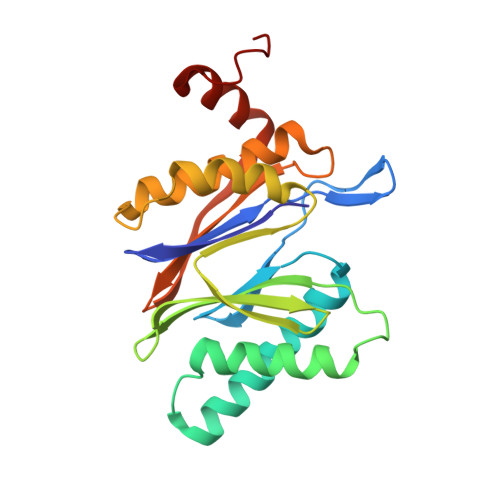
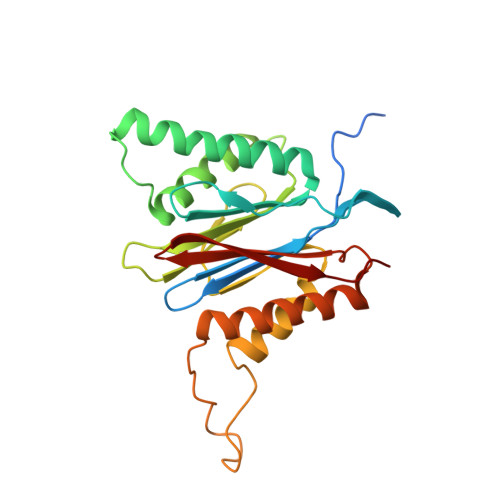
A gated channel into the proteasome core particle.
Groll, M., Bajorek, M., Kohler, A., Moroder, L., Rubin, D.M., Huber, R., Glickman, M.H., Finley, D.(2000) Nat Struct Biol 7: 1062-1067
- PubMed: 11062564
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/80992
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1G0U - PubMed Abstract:
The core particle (CP) of the yeast proteasome is composed of four heptameric rings of subunits arranged in a hollow, barrel-like structure. We report that the CP is autoinhibited by the N-terminal tails of the outer (alpha) ring subunits. Crystallographic analysis showed that deletion of the tail of the alpha 3-subunit opens a channel into the proteolytically active interior chamber of the CP, thus derepressing peptide hydrolysis. In the latent state of the particle, the tails prevent substrate entry by imposing topological closure on the CP. Inhibition by the alpha-subunit tails is relieved upon binding of the regulatory particle to the CP to form the proteasome holoenzyme.
- Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, D-82152 Martinsried, Germany. groll@biochem.mdg.de
Organizational Affiliation: