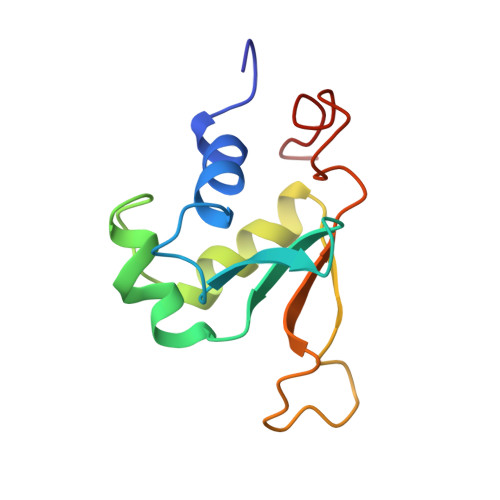
Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of Drosophila heat shock transcription factor.
Vuister, G.W., Kim, S.J., Orosz, A., Marquardt, J., Wu, C., Bax, A.(1994) Nat Struct Biol 1: 605-614
- PubMed: 7634100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1HKS, 1HKT - PubMed Abstract:
The solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the Drosophila heat shock transcription factor, as determined by multidimensional multinuclear NMR, resembles that of the helix-turn-helix class of DNA-binding proteins. The domain comprises a four-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet, packed against a three-helix bundle. The second helix is significantly distorted and is separated from the third helix by an extended turn which is subject to conformational averaging on an intermediate time scale. Helix 3 forms a classical amphipathic helix with polar and charged residues exposed to the solvent. Upon titration with DNA, resonance shifts in the backbone and Asn and Gln side-chain amides indicate that helix 3 acts as the recognition helix of the heat shock transcription factor.
- Laboratory of Chemical Physics, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20892, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: