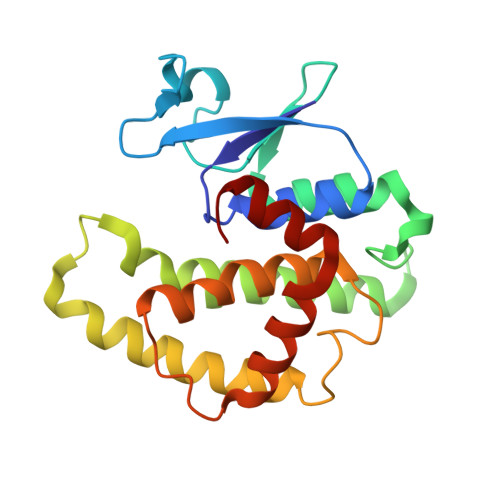
Conserved structural elements in glutathione transferase homologues encoded in the genome of Escherichia coli
Rife, C.L., Parsons, J.F., Xiao, G., Gilliland, G.L., Armstrong, R.N.(2003) Proteins 53: 777-782
- PubMed: 14635120
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.10452
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1N2A - PubMed Abstract:
Multiple sequence alignments of the eight glutathione (GSH) transferase homologues encoded in the genome of Escherichia coli were used to define a consensus sequence for the proteins. The consensus sequence was analyzed in the context of the three-dimensional structure of the gst gene product (EGST) obtained from two different crystal forms of the enzyme. The enzyme consists of two domains. The N-terminal region (domain I) has a thioredoxin-like alpha/beta-fold, while the C-terminal domain (domain II) is all alpha-helical. The majority of the consensus residues (12/17) reside in the N-terminal domain. Fifteen of the 17 residues are involved in hydrophobic core interactions, turns, or electrostatic interactions between the two domains. The results suggest that all of the homologues retain a well-defined group of structural elements both in and between the N-terminal alpha/beta domain and the C-terminal domain. The conservation of two key residues for the recognition motif for the gamma-glutamyl-portion of GSH indicates that the homologues may interact with GSH or GSH analogues such as glutathionylspermidine or alpha-amino acids. The genome context of two of the homologues forms the basis for a hypothesis that the b2989 and yibF gene products are involved in glutathionylspermidine and selenium biochemistry, respectively.
- Department of Biochemistry and the Center in Molecular Toxicology, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville Tennessee 37232-0146, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: