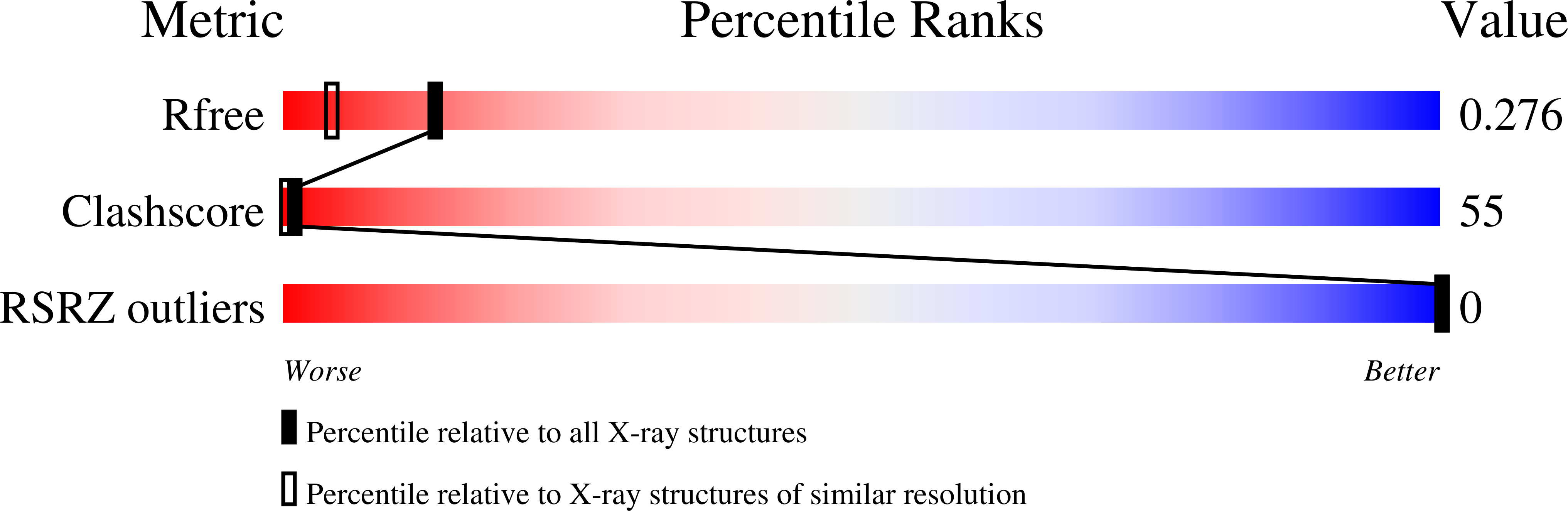Influence of minor groove substituents on the structure of DNA holliday junctions.
Hays, F.A., Jones, Z.J., Ho, P.S.(2004) Biochemistry 43: 9813-9822
- PubMed: 15274635
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi049461d
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1S1K, 1S1L - PubMed Abstract:
The inosine-containing sequence d(CCIGTACm(5)CGG) is shown to crystallize as a four-stranded DNA junction. This structure is nearly identical to the antiparallel junction formed by the parent d(CCGGTACm(5)()CGG) sequence [Vargason, J. M., and Ho, P. S. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 21041-21049] in terms of its conformational geometry, and inter- and intramolecular interactions within the DNA and between the DNA and solvent, even though the 2-amino group in the minor groove of the important G(3).m(5)C(8) base pair of the junction core trinucleotide (italicized) has been removed. In contrast, the analogous 2,6-diaminopurine sequence d(CCDGTACTGG) crystallizes as resolved duplex DNAs, just like its parent sequence d(CCAGTACTGG) [Hays, F. A., Vargason, J. M., and Ho, P. S. (2003) Biochemistry 42, 9586-9597]. These results demonstrate that it is not the presence or absence of the 2-amino group in the minor groove of the R(3).Y(8) base pair that specifies whether a sequence forms a junction, but the positions of the extracyclic amino and keto groups in the major groove. Finally, the study shows that the arms of the junction can accommodate perturbations to the B-DNA conformation of the stacked duplex arms associated with the loss of the 2-amino substituent, and that two hydrogen bonding interactions from the C(7) and Y(8) pyrimidine nucleotides to phosphate oxygens of the junction crossover specify the geometry of the Holliday junction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, ALS 2011, Oregon State University, Corvallis, Oregon 97331, USA.