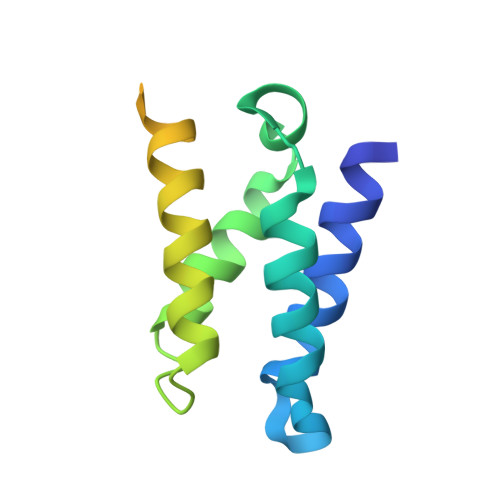
Solution structure of the HIV-1 integrase-binding domain in LEDGF/p75
Cherepanov, P., Sun, Z.-Y.J., Rahman, S., Maertens, G., Wagner, G., Engelman, A.(2005) Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 526-532
- PubMed: 15895093
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb937
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Z9E - PubMed Abstract:
Lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF)/p75 is the dominant binding partner of HIV-1 integrase (IN) in human cells. We have determined the NMR structure of the integrase-binding domain (IBD) in LEDGF and identified amino acid residues essential for the interaction. The IBD is a compact right-handed bundle composed of five alpha-helices. Based on folding topology, the IBD is structurally related to a diverse family of alpha-helical proteins that includes eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4G and karyopherin-beta. LEDGF residues essential for the interaction with IN were localized to interhelical loop regions of the bundle structure. Interaction-defective IN mutants were previously shown to cripple replication although they retained catalytic function. The initial structure determination of a host cell factor that tightly binds to a retroviral enzyme lays the groundwork for understanding enzyme-host interactions important for viral replication.
- Department of Cancer Immunology and AIDS, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 44 Binney Street, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: