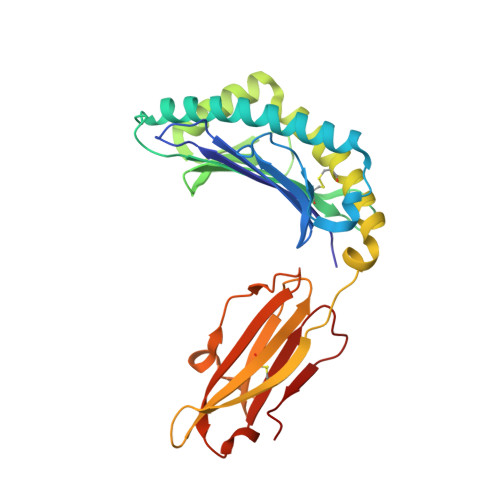
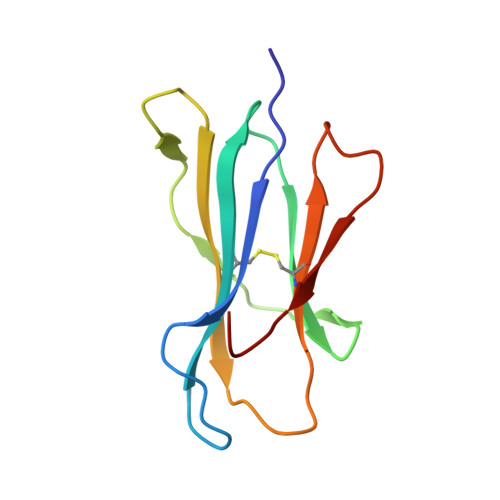
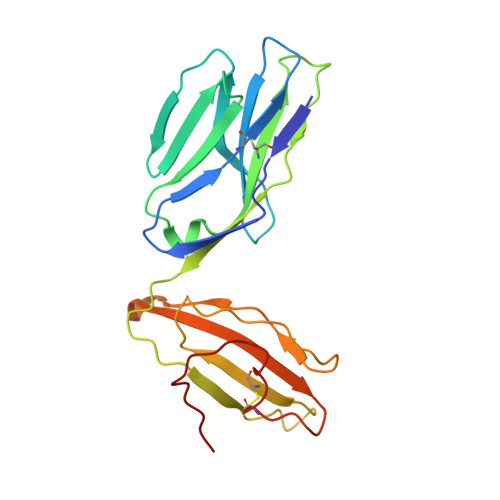
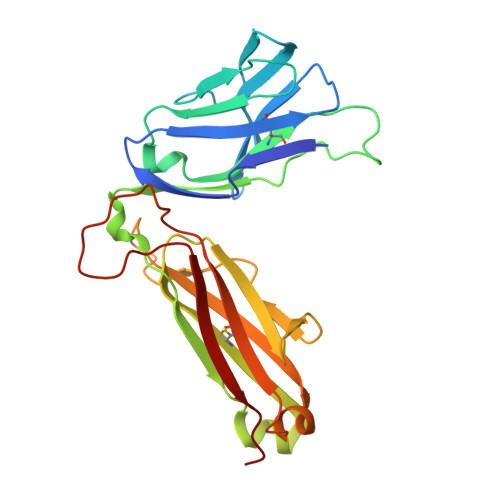
T cell receptor recognition of a 'super-bulged' major histocompatibility complex class I-bound peptide
Tynan, F.E., Burrows, S.R., Buckle, A.M., Clements, C.S., Borg, N.A., Miles, J.J., Beddoe, T., Whisstock, J.C., Wilce, M.C., Silins, S.L., Burrows, J.M., Kjer-Nielsen, L., Kostenko, L., Purcell, A.W., McCluskey, J., Rossjohn, J.(2005) Nat Immunol 6: 1114-1122
- PubMed: 16186824
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1257
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AK4 - PubMed Abstract:
Unusually long major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted epitopes are important in immunity, but their 'bulged' conformation represents a potential obstacle to alphabeta T cell receptor (TCR)-MHC class I docking. To elucidate how such recognition is achieved while still preserving MHC restriction, we have determined here the structure of a TCR in complex with HLA-B(*)3508 presenting a peptide 13 amino acids in length. This complex was atypical of TCR-peptide-MHC class I interactions, being dominated at the interface by peptide-mediated interactions. The TCR assumed two distinct orientations, swiveling on top of the centrally bulged, rigid peptide such that only limited contacts were made with MHC class I. Although the TCR-peptide recognition resembled an antibody-antigen interaction, the TCR-MHC class I contacts defined a minimal 'generic footprint' of MHC-restriction. Thus our findings simultaneously demonstrate the considerable adaptability of the TCR and the 'shape' of MHC restriction.
- The Protein Crystallography Unit, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Biomedical Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria 3800, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: