Electron Transfer Complex Formation between Oxygenase and Ferredoxin Components in Rieske Nonheme Iron Oxygenase System
Ashikawa, Y., Fujimoto, Z., Noguchi, H., Habe, H., Omori, T., Yamane, H., Nojiri, H.(2006) Structure 14: 1779-1789
- PubMed: 17161368
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2006.10.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DE5, 2DE6, 2DE7 - PubMed Abstract:
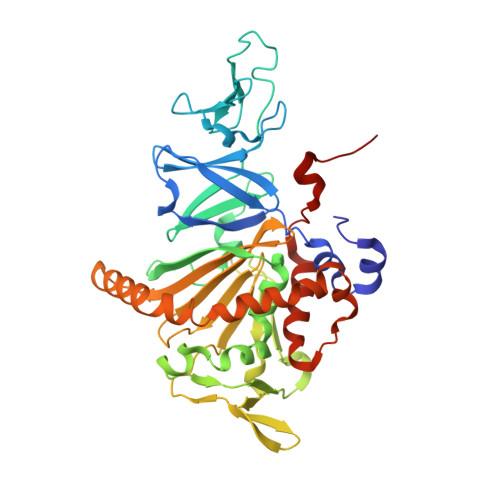
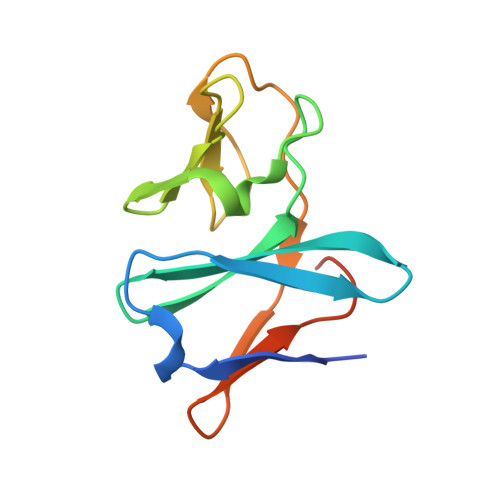
Carbazole 1,9a-dioxygenase (CARDO), a member of the Rieske nonheme iron oxygenase system (ROS), consists of a terminal oxygenase (CARDO-O) and electron transfer components (ferredoxin [CARDO-F] and ferredoxin reductase [CARDO-R]). We determined the crystal structures of the nonreduced, reduced, and substrate-bound binary complexes of CARDO-O with its electron donor, CARDO-F, at 1.9, 1.8, and 2.0 A resolutions, respectively. These structures provide the first structure-based interpretation of intercomponent electron transfer between two Rieske [2Fe-2S] clusters of ferredoxin and oxygenase in ROS. Three molecules of CARDO-F bind to the subunit boundary of one CARDO-O trimeric molecule, and specific binding created by electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions with conformational changes suitably aligns the two Rieske clusters for electron transfer. Additionally, conformational changes upon binding carbazole resulted in the closure of a lid over the substrate-binding pocket, thereby seemingly trapping carbazole at the substrate-binding site.
- Biotechnology Research Center, The University of Tokyo, 1-1-1 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8657, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: