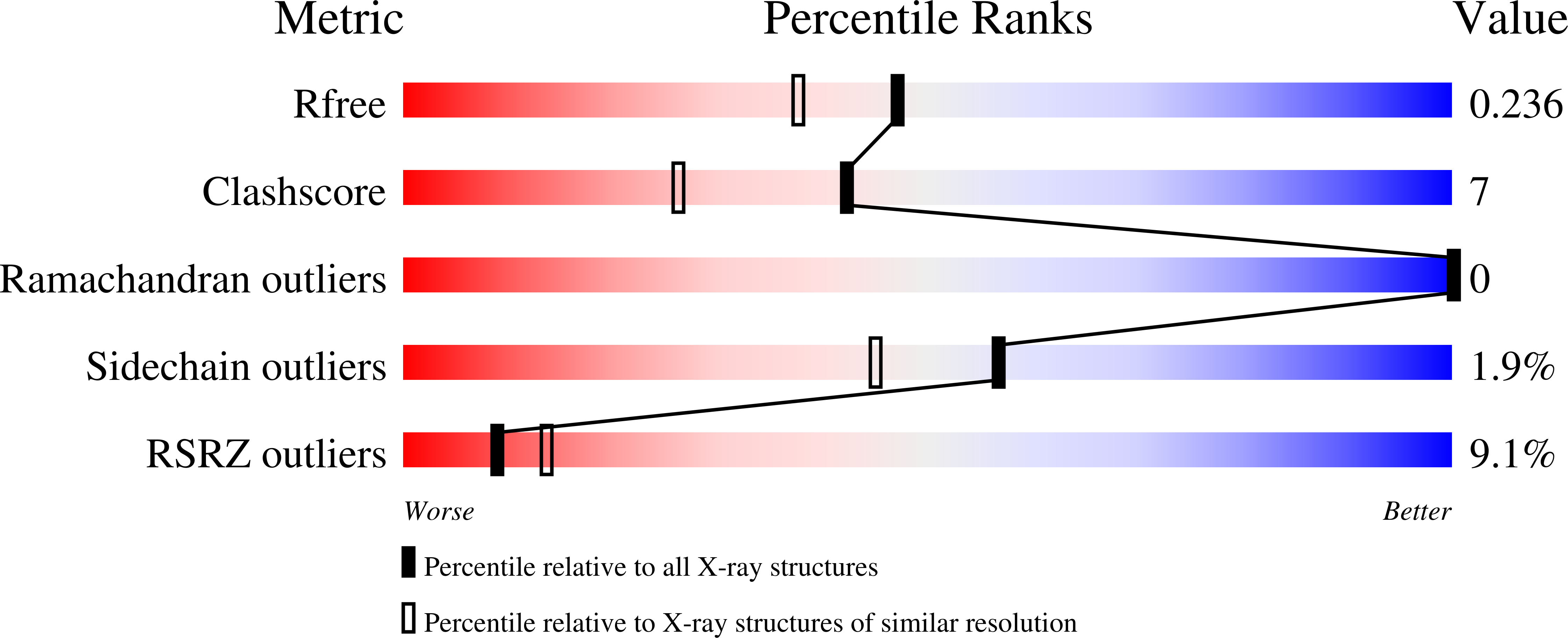
Identification of a novel and potent inhibitor of phospholipase A(2) in a medicinal plant: crystal structure at 1.93A and Surface Plasmon Resonance analysis of phospholipase A(2) complexed with berberine
Chandra, D.N., Prasanth, G.K., Singh, N., Kumar, S., Jithesh, O., Sadasivan, C., Sharma, S., Singh, T.P., Haridas, M.(2011) Biochim Biophys Acta 1814: 657-663
- PubMed: 21420512
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.03.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QVD - PubMed Abstract:
Crystal of Russell Viper venom phospholipase A(2) complexed with an isoquinoline alkaloid, berberine from a herbaceous plant Cardiospermum halicacabum, was prepared and its structure was solved by X-ray crystallography. The crystal diffracted up to 1.93Å and the structure solution clearly located the position of berberine in the active site of the enzyme. Two hydrogen bonds, one direct and the other water mediated, were formed between berberine and the enzyme. Gly 30 and His 48 made these two hydrogen bonds. Additionally, the hydrophobic surface of berberine made a number of hydrophobic contacts with side chains of neighboring amino acids. Surface Plasmon Resonance studies revealed strong binding affinity between berberine and phospholipase A(2). Enzyme inhibition studies proved that berberine is a competitive inhibitor of phospholipase A(2). It was inferred that the isoquinoline alkaloid, berberine, is a potent natural inhibitor of phospholipaseA(2).
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biotechnology & Microbiology, Kannur University, Palayad, Kerala 670661, India.