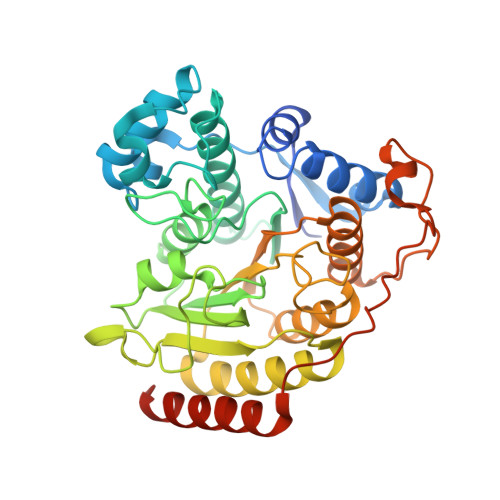
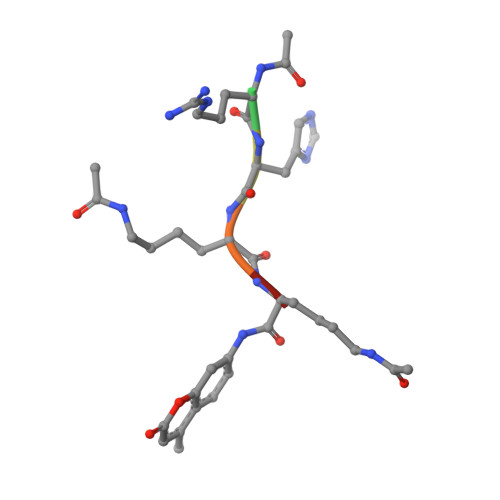
Substrate Binding to Histone Deacetylases as Revealed by Crystal Structure of Hdac8-Substrate Complex
Vannini, A., Volpari, C., Gallinari, P., Jones, P., Mattu, M., Carfi, A., Defrancesco, R., Steinkuhler, C., Di Marco, S.(2007) EMBO Rep 8: 879
- PubMed: 17721440
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7401047
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V5W, 2V5X - PubMed Abstract:
Histone deacetylases (HDACs)-an enzyme family that deacetylates histones and non-histone proteins-are implicated in human diseases such as cancer, and the first-generation of HDAC inhibitors are now in clinical trials. Here, we report the 2.0 A resolution crystal structure of a catalytically inactive HDAC8 active-site mutant, Tyr306Phe, bound to an acetylated peptidic substrate. The structure clarifies the role of active-site residues in the deacetylation reaction and substrate recognition. Notably, the structure shows the unexpected role of a conserved residue at the active-site rim, Asp 101, in positioning the substrate by directly interacting with the peptidic backbone and imposing a constrained cis-conformation. A similar interaction is observed in a new hydroxamate inhibitor-HDAC8 structure that we also solved. The crucial role of Asp 101 in substrate and inhibitor recognition was confirmed by activity and binding assays of wild-type HDAC8 and Asp101Ala, Tyr306Phe and Asp101Ala/Tyr306Phe mutants.
- Istituto di Ricerche di Biologia Molecolare P. Angeletti, Via Pontina Km 30.600, 00040 Pomezia, Rome, Italy.
Organizational Affiliation: