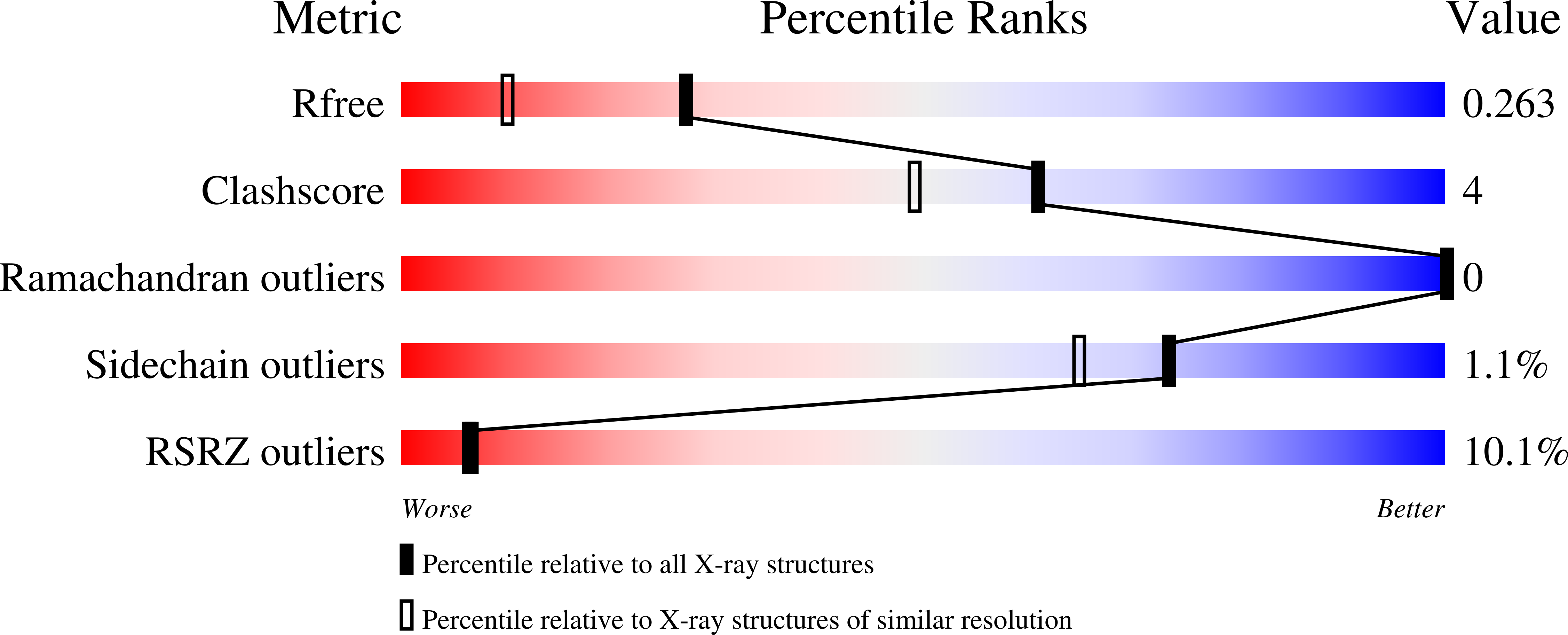
The Crystal Structure of the Leishmania Major Deoxyuridine Triphosphate Nucleotidohydrolase in Complex with Nucleotide Analogues, Dump, and Deoxyuridine.
Hemsworth, G.R., Moroz, O.V., Fogg, M.J., Scott, B., Bosch-Navarrete, C., Gonzalez-Pacanowska, D., Wilson, K.S.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 16470
- PubMed: 21454646
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.224873
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2CIC, 2CJE, 2YAY, 2YAZ, 2YB0 - PubMed Abstract:
Members of the Leishmania genus are the causative agents of the life-threatening disease leishmaniasis. New drugs are being sought due to increasing resistance and adverse side effects with current treatments. The knowledge that dUTPase is an essential enzyme and that the all α-helical dimeric kinetoplastid dUTPases have completely different structures compared with the trimeric β-sheet type dUTPase possessed by most organisms, including humans, make the dimeric enzymes attractive drug targets. Here, we present crystal structures of the Leishmania major dUTPase in complex with substrate analogues, the product dUMP and a substrate fragment, and of the homologous Campylobacter jejuni dUTPase in complex with a triphosphate substrate analogue. The metal-binding properties of both enzymes are shown to be dependent upon the ligand identity, a previously unseen characteristic of this family. Furthermore, structures of the Leishmania enzyme in the presence of dUMP and deoxyuridine coupled with tryptophan fluorescence quenching indicate that occupation of the phosphate binding region is essential for induction of the closed conformation and hence for substrate binding. These findings will aid in the development of dUTPase inhibitors as potential new lead anti-trypanosomal compounds.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, University of York, Heslington, York, United Kingdom.