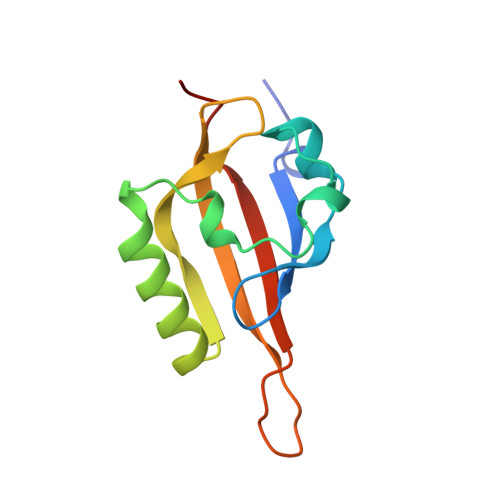
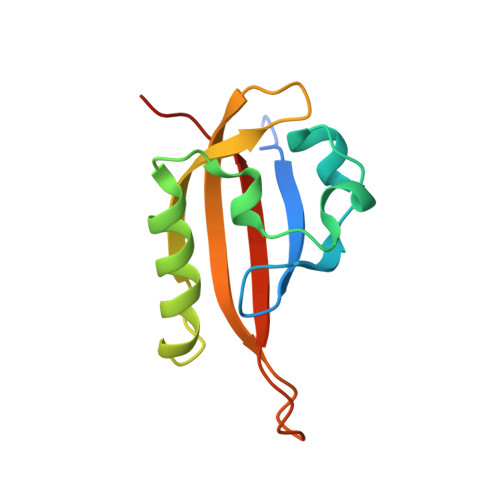
Artificial ligand binding within the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain of the HIF2 transcription factor.
Scheuermann, T.H., Tomchick, D.R., Machius, M., Guo, Y., Bruick, R.K., Gardner, K.H.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 450-455
- PubMed: 19129502
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808092106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3F1N, 3F1O, 3F1P - PubMed Abstract:
The hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) basic helix-loop-helix Per-aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT)-Sim (bHLH-PAS) transcription factors are master regulators of the conserved molecular mechanism by which metazoans sense and respond to reductions in local oxygen concentrations. In humans, HIF is critically important for the sustained growth and metastasis of solid tumors. Here, we describe crystal structures of the heterodimer formed by the C-terminal PAS domains from the HIF2alpha and ARNT subunits of the HIF2 transcription factor, both in the absence and presence of an artificial ligand. Unexpectedly, the HIF2alpha PAS-B domain contains a large internal cavity that accommodates ligands identified from a small-molecule screen. Binding one of these ligands to HIF2alpha PAS-B modulates the affinity of the HIF2alpha:ARNT PAS-B heterodimer in vitro. Given the essential role of PAS domains in forming active HIF heterodimers, these results suggest a presently uncharacterized ligand-mediated mechanism for regulating HIF2 activity in endogenous and clinical settings.
- Departments of Biochemistry and Pharmacology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, 5323 Harry Hines Boulevard, Dallas, TX 75390, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: