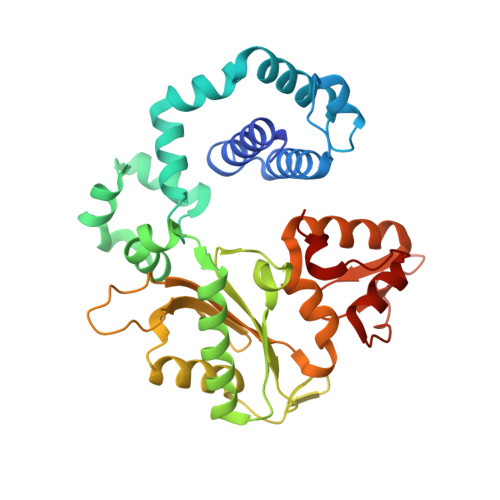
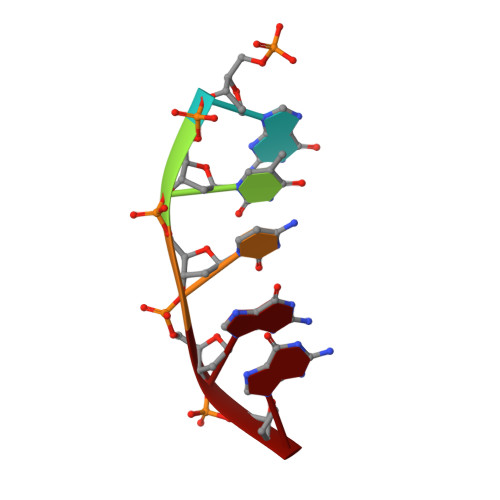
Amino Acid Substitution in the Active Site of DNA Polymerase beta Explains the Energy Barrier of the Nucleotidyl Transfer Reaction.
Batra, V.K., Perera, L., Lin, P., Shock, D.D., Beard, W.A., Pedersen, L.C., Pedersen, L.G., Wilson, S.H.(2013) J Am Chem Soc 135: 8078-8088
- PubMed: 23647366
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja403842j
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4JWM, 4JWN - PubMed Abstract:
DNA polymerase β (pol β) is a bifunctional enzyme widely studied for its roles in base excision DNA repair, where one key function is gap-filling DNA synthesis. In spite of significant progress in recent years, the atomic level mechanism of the DNA synthesis reaction has remained poorly understood. Based on crystal structures of pol β in complex with its substrates and theoretical considerations of amino acids and metals in the active site, we have proposed that a nearby carboxylate group of Asp256 enables the reaction by accepting a proton from the primer O3'group, thus activating O3'as the nucleophile in the reaction path. Here, we tested this proposal by altering the side chain of Asp256 to Glu and then exploring the impact of this conservative change on the reaction. The D256E enzyme is more than 1000-fold less active than the wild-type enzyme, and the crystal structures are subtly different in the active sites of the D256E and wild-type enzymes. Theoretical analysis of DNA synthesis by the D256E enzyme shows that the O3'proton still transfers to the nearby carboxylate of residue 256. However, the electrostatic stabilization and location of the O3' proton transfer during the reaction path are dramatically altered compared with wild-type. Surprisingly, this is due to repositioning of the Arg254 side chain in the Glu256 enzyme active site, such that Arg254 is not in position to stabilize the proton transfer from O3'. The theoretical results with the wild-type enzyme indicate an early charge reorganization associated with the O3' proton transfer, and this does not occur in the D256E enzyme. The charge reorganization is mediated by the catalytic magnesium ion in the active site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Biology, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, P.O. Box 12233, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709-12233, USA.