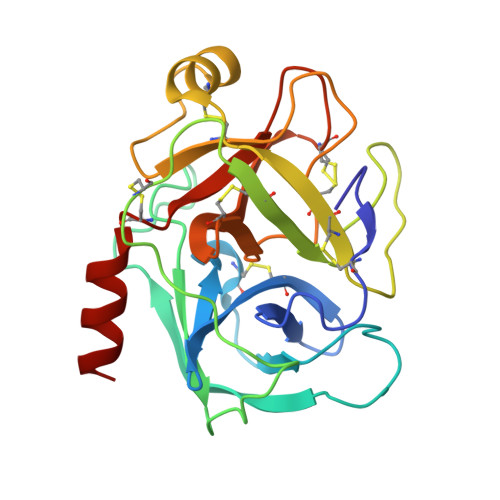
Atomic resolution crystal structure of HV-BBI protease inhibitor from amphibian skin in complex with bovine trypsin.
Grudnik, P., Debowski, D., Legowska, A., Malicki, S., Golik, P., Karna, N., Rolka, K., Dubin, G.(2015) Proteins 83: 582-589
- PubMed: 25546528
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.24750
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4U2W - PubMed Abstract:
Protease inhibitors of the Bowman-Birk (BBI) family are commonly found in plants and animals where they play a protective role against invading pathogens. Here, we report an atomic resolution (1Å) crystal structure of a peptide inhibitor isolated from a skin secretion of a Chinese bamboo odorous frog Huia versabilis (HV-BBI) in complex with trypsin. HV-BBI shares significant similarities in sequence with a previously described inhibitor from a diskless-fingered odorous frog Odorrana graham (ORB). However, the latter is characterized by more than a 16,000 fold higher Ki against trypsin than HV-BBI. Comparative analysis of trypsin cocrystal structures of HV-BBI and ORB and additionally that of Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor (SFTI-1) together with accessory information on the affinities of inhibitor variants allowed us to pinpoint the inhibitor moiety responsible for the observed large difference in activity and also to define the extent of modifications permissible within the common protease-binding loop scaffold of BBI inhibitors. We suggest that modifications outside of the inhibitory loop permit the evolution of specificity toward different enzymes characterized by trypsin-like specificity.
- Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Biotechnology, Jagiellonian University, Krakow, 30-387, Poland.
Organizational Affiliation: