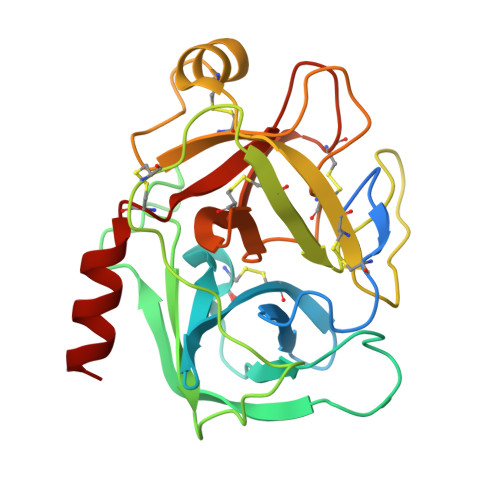
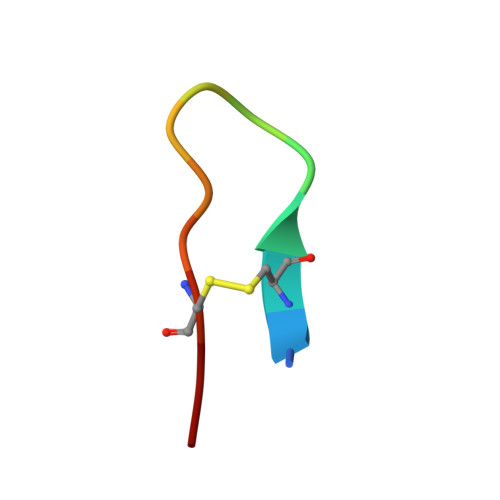
Investigation of Serine-Proteinase-Catalyzed Peptide Splicing in Analogues of Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor 1 (SFTI-1).
Karna, N., Legowska, A., Malicki, S., Debowski, D., Golik, P., Gitlin, A., Grudnik, P., Wladyka, B., Brzozowski, K., Dubin, G., Rolka, K.(2015) Chembiochem 16: 2036-2045
- PubMed: 26212347
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201500296
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XOJ - PubMed Abstract:
Serine-proteinase-catalyzed peptide splicing was demonstrated in analogues of the trypsin inhibitor SFTI-1: both single peptides and two-peptide chains (C- and N-terminal peptide chains linked by a disulfide bridge). In the second series, peptide splicing with catalytic amount of proteinase was observed only when formation of acyl-enzyme intermediate was preceded by hydrolysis of the substrate Lys-Ser peptide bond. Here we demonstrate that with an equimolar amount of the proteinase, splicing occurs in all the two-peptide-chain analogues. This conclusion was supported by high resolution crystal structures of selected analogues in complex with trypsin. We showed that the process followed a direct transpeptidation mechanism. Thus, the acyl-enzyme intermediate was formed and was immediately used for a new peptide bond formation; products associated with the hydrolysis of the acyl-enzyme were not observed. The peptide splicing was sequence- not structure-specific.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioorganic Chemistry, Faculty of Chemistry, University of Gdansk, Wita Stwosza 63, 80-308, Gdansk, Poland.