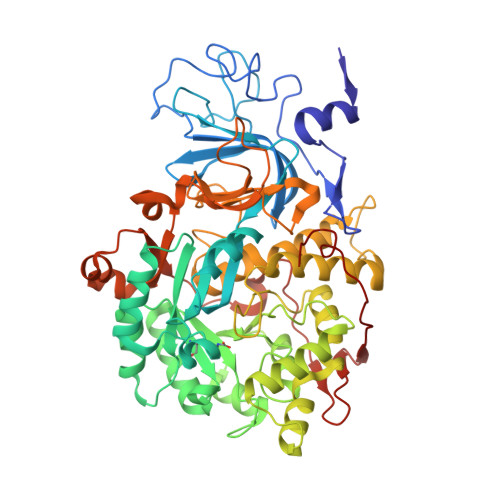
Inactivation of Urease by 1,4-Benzoquinone: Chemistry at the Protein Surface.
Mazzei, L., Cianci, M., Musiani, F., Ciurli, S.(2016) Dalton Trans 45: 5455
- PubMed: 26961812
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c6dt00652c
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5FSD, 5FSE - PubMed Abstract:
The high activity of urease, a Ni(ii) enzyme, has several adverse effects on human health and agriculture, and its modulation needs the use of inhibitors. 1,4-Benzoquinone (BQ) irreversibly inactivates Sporosarcina pasteurii urease (SPU), with first order kinetics for both the inhibitor and the enzyme. This reaction is stoichiometrically quenched in the presence of sulphite. The 2.07 Å crystal structure of SPU bound to BQ shows the presence of a 1,4-hydroquinone moiety covalently bound to the thiol group of αCys322, a key residue found on the mobile flap regulating the substrate access to the active site. The 1.75 Å crystal structure obtained when sulphite is added to a solution of SPU previously incubated with BQ shows the presence of a 2,5-dihydroxy-benzenesulphonate moiety bound to the αCys322 thiol group. These data reveal how the active site cysteine reacts with a prototypical BQ moiety, found in a large number of natural substances potentially suitable to control the urease activity.
- Laboratory of bioinorganic Chemistry, Department of Pharmacy and Biotechnology, University of Bologna, Viale G. Fanin 40, I-40127, Bologna, Italy. stefano.ciurli@unibo.it.
Organizational Affiliation: