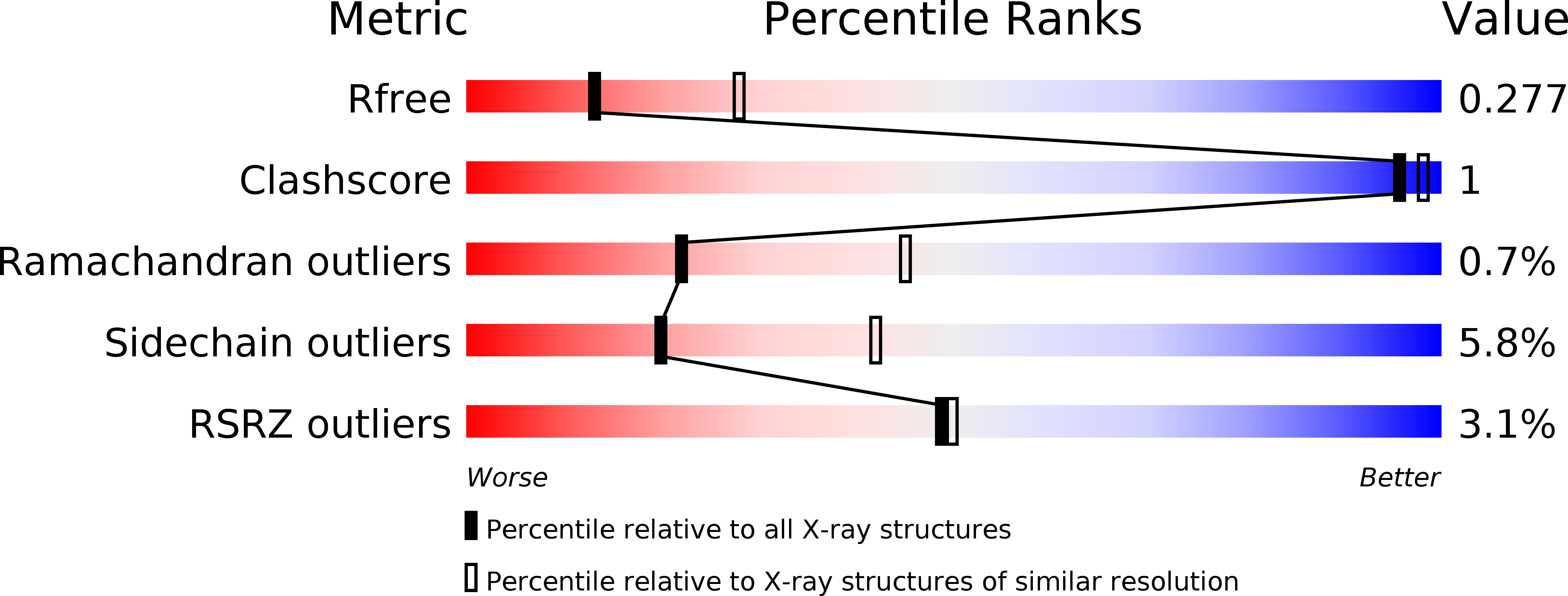
Discovery of potent SOS1 inhibitors that block RAS activation via disruption of the RAS-SOS1 interaction.
Hillig, R.C., Sautier, B., Schroeder, J., Moosmayer, D., Hilpmann, A., Stegmann, C.M., Werbeck, N.D., Briem, H., Boemer, U., Weiske, J., Badock, V., Mastouri, J., Petersen, K., Siemeister, G., Kahmann, J.D., Wegener, D., Bohnke, N., Eis, K., Graham, K., Wortmann, L., von Nussbaum, F., Bader, B.(2019) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116: 2551-2560
- PubMed: 30683722
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1812963116
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5OVD, 5OVE, 5OVF, 5OVG, 5OVH, 5OVI, 6EIE, 6EPL, 6EPM, 6EPN, 6EPO, 6EPP - PubMed Abstract:
Since the late 1980s, mutations in the RAS genes have been recognized as major oncogenes with a high occurrence rate in human cancers. Such mutations reduce the ability of the small GTPase RAS to hydrolyze GTP, keeping this molecular switch in a constitutively active GTP-bound form that drives, unchecked, oncogenic downstream signaling. One strategy to reduce the levels of active RAS is to target guanine nucleotide exchange factors, which allow RAS to cycle from the inactive GDP-bound state to the active GTP-bound form. Here, we describe the identification of potent and cell-active small-molecule inhibitors which efficiently disrupt the interaction between KRAS and its exchange factor SOS1, a mode of action confirmed by a series of biophysical techniques. The binding sites, mode of action, and selectivity were elucidated using crystal structures of KRAS G12C -SOS1, SOS1, and SOS2. By preventing formation of the KRAS-SOS1 complex, these inhibitors block reloading of KRAS with GTP, leading to antiproliferative activity. The final compound 23 (BAY-293) selectively inhibits the KRAS-SOS1 interaction with an IC 50 of 21 nM and is a valuable chemical probe for future investigations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research and Development, Pharmaceuticals, Bayer AG, 13353 Berlin, Germany; roman.hillig@bayer.com benjamin.bader@bayer.com.