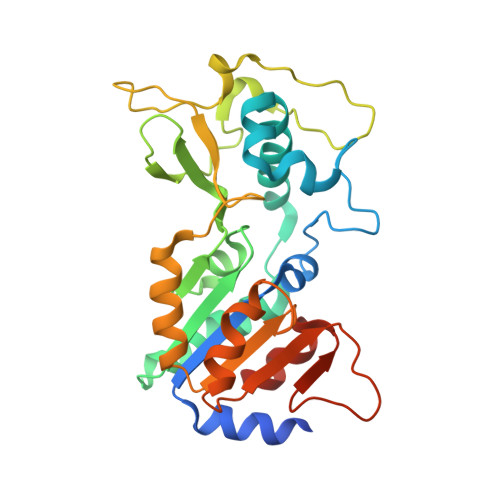
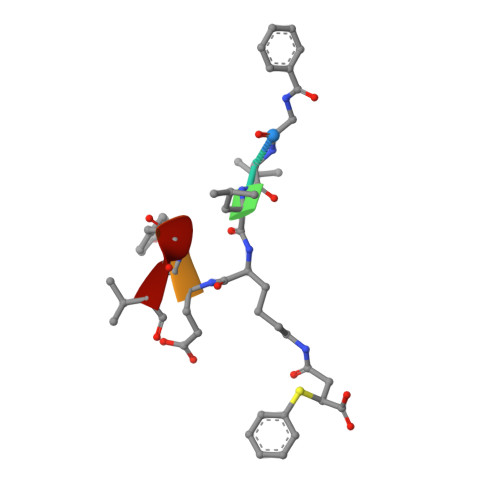
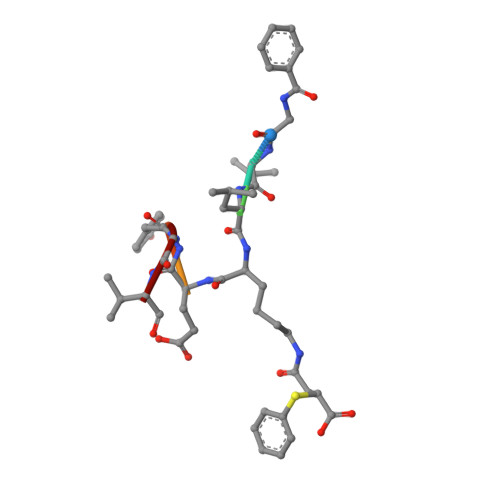
Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Human Sirtuin 5.
Kalbas, D., Liebscher, S., Nowak, T., Meleshin, M., Pannek, M., Popp, C., Alhalabi, Z., Bordusa, F., Sippl, W., Steegborn, C., Schutkowski, M.(2018) J Med Chem 61: 2460-2471
- PubMed: 29494161
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01648
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FKY, 6FKZ, 6FLG - PubMed Abstract:
Sirtuins are protein deacylases that regulate metabolism and stress responses and are implicated in aging-related diseases. Modulators of the human sirtuins Sirt1-7 are sought as chemical tools and potential therapeutics, e.g., for cancer. Selective and potent inhibitors are available for Sirt2, but selective inhibitors for Sirt5 with K i values in the low nanomolar range are lacking. We synthesized and screened 3-arylthiosuccinylated and 3-benzylthiosuccinylated peptide derivatives yielding Sirt5 inhibitors with low-nanomolar K i values. A biotinylated derivative with this scaffold represents an affinity probe for human Sirt5 that is able to selectively extract this enzyme out of complex biological samples like cell lysates. Crystal structures of Sirt5/inhibitor complexes reveal that the compounds bind in an unexpected manner to the active site of Sirt5.
- Department of Enzymology, Institute of Biochemistry and Biotechnology , Martin-Luther-University Halle-Wittenberg , 06120 Halle/Saale , Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: