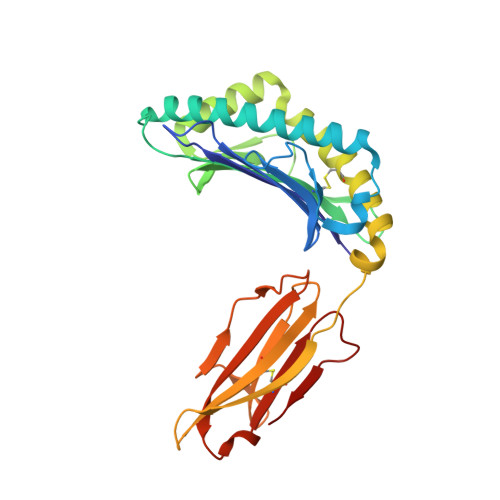
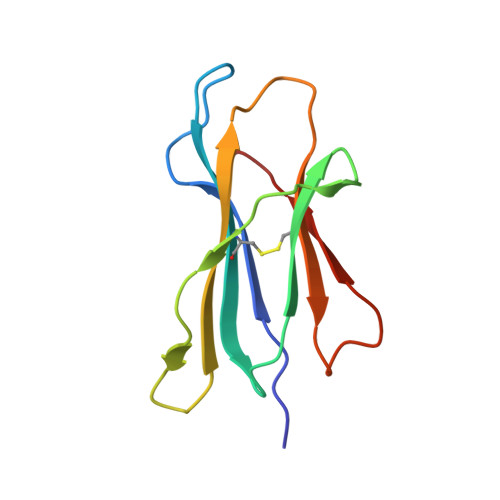
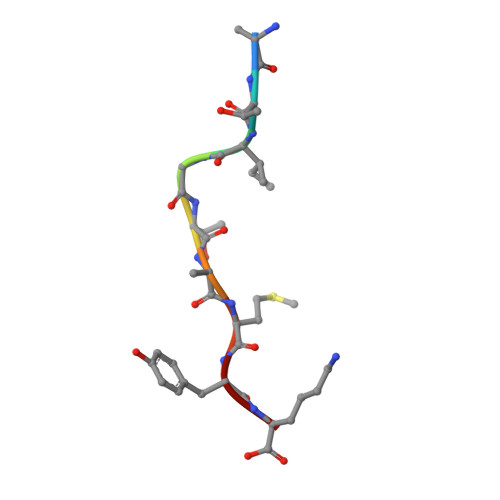
Crystal structure of suboptimal viral fragments of Epstein Barr Virus Rta peptide-HLA complex that stimulate CD8 T cell response.
Huan, X., Zhuo, Z., Xiao, Z., Ren, E.C.(2019) Sci Rep 9: 16660-16660
- PubMed: 31723204
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53201-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JOZ, 6JP3 - PubMed Abstract:
Peptides presented by Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class-I molecules are generally 8-10 amino acids in length. However, the predominant pool of peptide fragments generated by proteasomes is less than 8 amino acids in length. Using the Epstein - Barr virus (EBV) Rta-epitope (ATIGTAMYK, residues 134-142) restricted by HLA-A*11:01 which generates a strong immunodominant response, we investigated the minimum length of a viral peptide that can constitute a viral epitope recognition by CD8 T cells. The results showed that Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors can be stimulated by a viral peptide fragment as short as 4-mer (AMYK), together with a 5-mer (ATIGT) to recapitulate the full length EBV Rta epitope. This was confirmed by generating crystals of the tetra-complex (2 peptides, HLA and β2-microglobulin). The solved crystal structure of HLA-A*11:01 in complex with these two short peptides revealed that they can bind in the same orientation similar to parental peptide (9-mer) and the free ends of two short peptides acquires a bulged conformation that is directed towards the T cell receptor. Our data shows that suboptimal length of 4-mer and 5-mer peptides can complement each other to form a stable peptide-MHC (pMHC) complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Singapore Immunology Network, 8A Biomedical Grove, #03-06 Immunos, Singapore, 138648, Singapore.