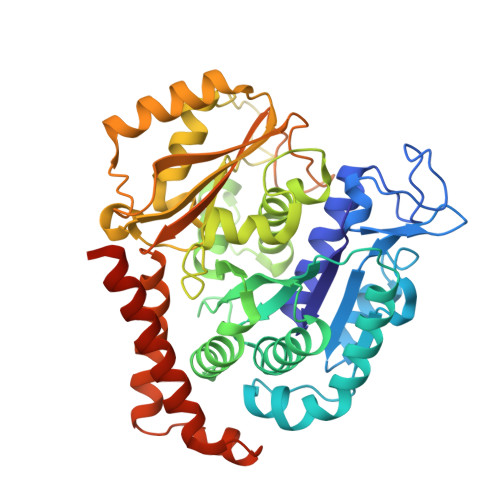
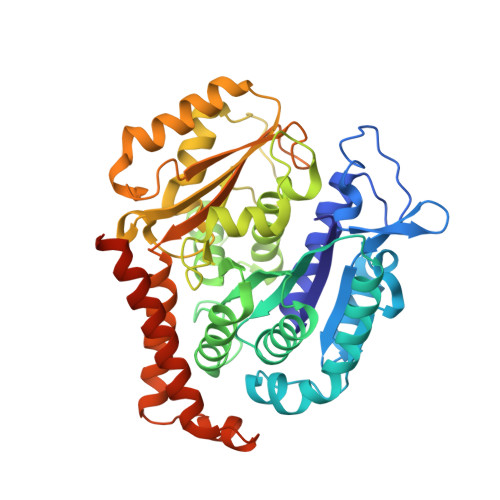
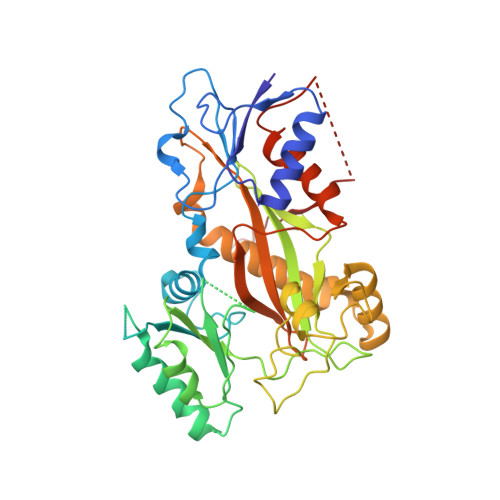
X-ray Crystal Structure Guided Discovery and Antitumor Efficacy of Dihydroquinoxalinone as Potent Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors.
Arnst, K.E., Banerjee, S., Wang, Y., Chen, H., Li, Y., Yang, L., Li, W., Miller, D.D., Li, W.(2019) ACS Chem Biol 14: 2810-2821
- PubMed: 31714738
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00696
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6N47 - PubMed Abstract:
Because of its multifaceted role in cellular functions, tubulin is a validated and productive drug target for cancer therapy. While many tubulin inhibitors demonstrate clinical efficacy, they are often limited by the development of multidrug resistance. Therefore, implementation of tubulin inhibitors that can overcome resistance could provide significant therapeutic benefits. To optimize our previously reported tubulin inhibitor, 4a , we designed and synthesized two new analogues, SB202 and SB204 , based on the crystal structure of 4a in complex with tubulin protein. SB202 and SB204 achieved enhanced binding at the colchicine site in tubulin and also showed improved metabolic stability and antiproliferative potency in vitro . Functional studies confirmed that SB202 and SB204 inhibit tubulin polymerization, arrest cells in the G 2 /M phase of the cell cycle, interfere with cancer cell migration and proliferation, and enhance apoptotic cascades. When evaluated in vivo , SB202 exhibited antitumor and vascular disrupting action against paclitaxel-resistant mouse xenograft models, strongly suggesting the potential of this scaffold to overcome multidrug resistance for cancer therapy.
- Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy , University of Tennessee Health Science Center , Memphis , Tennessee 38163 , United States.
Organizational Affiliation: