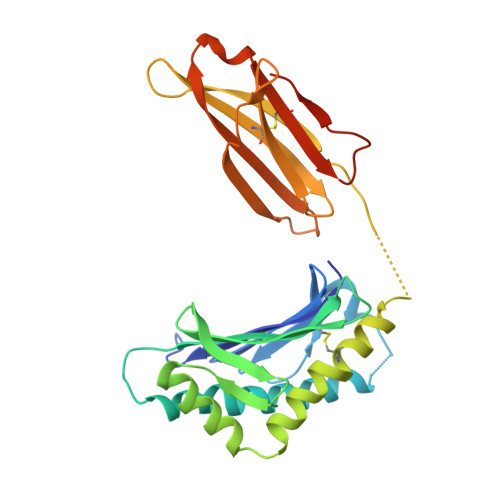
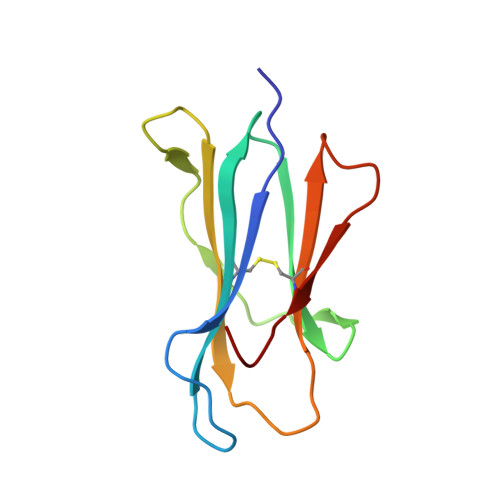
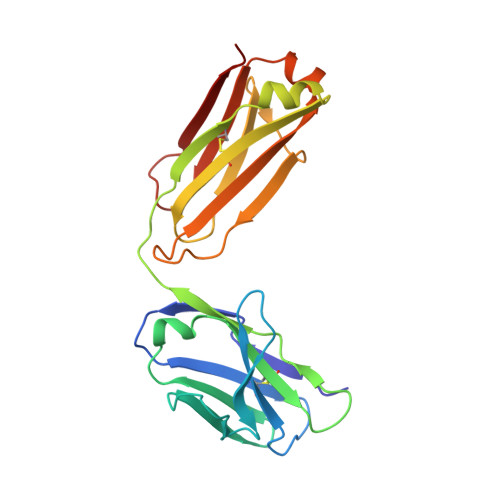
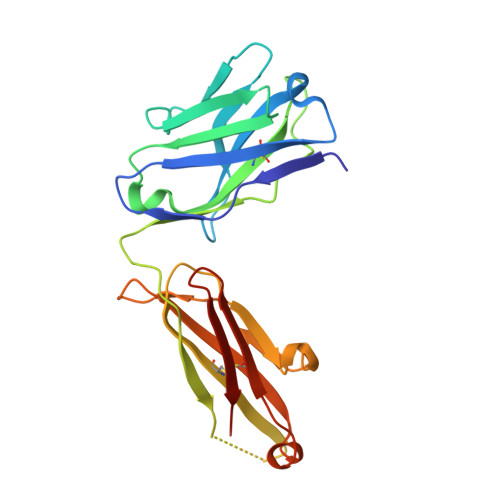
Blocking FcRn in humans reduces circulating IgG levels and inhibits IgG immune complex-mediated immune responses.
Blumberg, L.J., Humphries, J.E., Jones, S.D., Pearce, L.B., Holgate, R., Hearn, A., Cheung, J., Mahmood, A., Del Tito, B., Graydon, J.S., Stolz, L.E., Bitonti, A., Purohit, S., de Graaf, D., Kacena, K., Andersen, J.T., Christianson, G.J., Roopenian, D.C., Hubbard, J.J., Gandhi, A.K., Lasseter, K., Pyzik, M., Blumberg, R.S.(2019) Sci Adv 5: eaax9586-eaax9586
- PubMed: 31897428
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax9586
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NHA - PubMed Abstract:
The neonatal crystallizable fragment receptor (FcRn) functions as an intracellular protection receptor for immunoglobulin G (IgG). Recently, several clinical studies have reported the lowering of circulating monomeric IgG levels through FcRn blockade for the potential treatment of autoimmune diseases. Many autoimmune diseases, however, are derived from the effects of IgG immune complexes (ICs). We generated, characterized, and assessed the effects of SYNT001, a FcRn-blocking monoclonal antibody, in mice, nonhuman primates (NHPs), and humans. SYNT001 decreased all IgG subtypes and IgG ICs in the circulation of humans, as we show in a first-in-human phase 1, single ascending dose study. In addition, IgG IC induction of inflammatory pathways was dependent on FcRn and inhibited by SYNT001. These studies expand the role of FcRn in humans by showing that it controls not only IgG protection from catabolism but also inflammatory pathways associated with IgG ICs involved in a variety of autoimmune diseases.
- Syntimmune Inc., Boston, MA 02116, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: