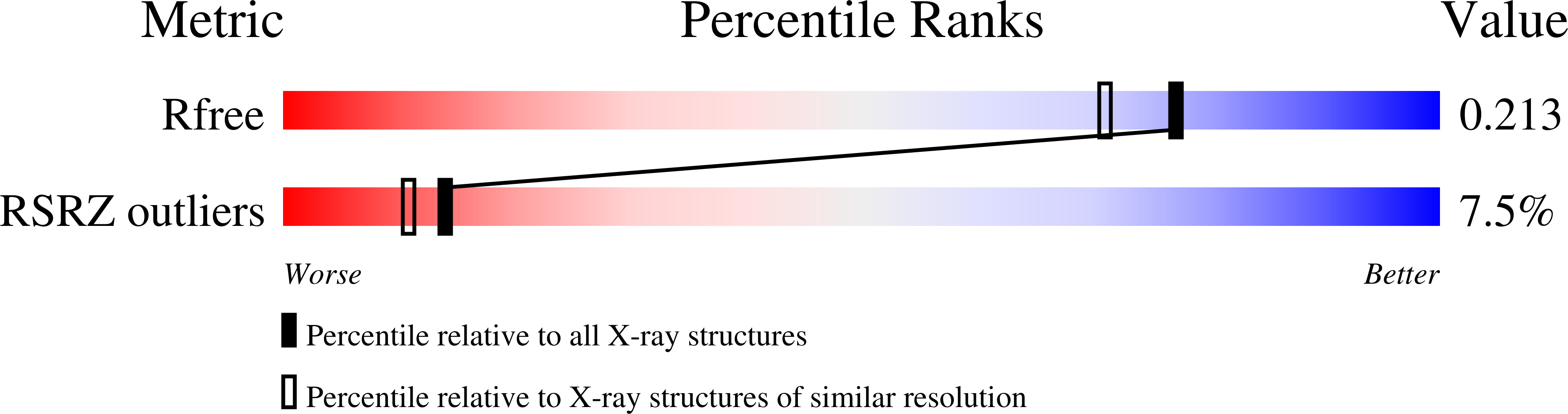High Affinity Binding of N2-Modified Guanine Derivatives Significantly Disrupts the Ligand Binding Pocket of the Guanine Riboswitch.
Matyjasik, M.M., Hall, S.D., Batey, R.T.(2020) Molecules 25
- PubMed: 32414072
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25102295
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6UBU, 6UC7, 6UC8, 6UC9 - PubMed Abstract:
Riboswitches are important model systems for the development of approaches to search for RNA-targeting therapeutics. A principal challenge in finding compounds that target riboswitches is that the effector ligand is typically almost completely encapsulated by the RNA, which severely limits the chemical space that can be explored. Efforts to find compounds that bind the guanine/adenine class of riboswitches with a high affinity have in part focused on purines modified at the C6 and C2 positions. These studies have revealed compounds that have low to sub-micromolar affinity and, in a few cases, have antimicrobial activity. To further understand how these compounds interact with the guanine riboswitch, we have performed an integrated structural and functional analysis of representative guanine derivatives with modifications at the C8, C6 and C2 positions. Our data indicate that while modifications of guanine at the C6 position are generally unfavorable, modifications at the C8 and C2 positions yield compounds that rival guanine with respect to binding affinity. Surprisingly, C2-modified guanines such as N 2-acetylguanine completely disrupt a key Watson-Crick pairing interaction between the ligand and RNA. These compounds, which also modulate transcriptional termination as efficiently as guanine, open up a significant new chemical space of guanine modifications in the search for antimicrobial agents that target purine riboswitches.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Colorado, Boulder, Colorado, CO 80309, USA.