The exploration of aza-quinolines as hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (H-PGDS) inhibitors with low brain exposure.
Cadilla, R., Deaton, D.N., Do, Y., Elkins, P.A., Ennulat, D., Guss, J.H., Holt, J., Jeune, M.R., King, A.G., Klapwijk, J.C., Kramer, H.F., Kramer, N.J., Laffan, S.B., Masuria, P.I., McDougal, A.V., Mortenson, P.N., Musetti, C., Peckham, G.E., Pietrak, B.L., Poole, C., Price, D.J., Rendina, A.R., Sati, G., Saxty, G., Shearer, B.G., Shewchuk, L.M., Sneddon, H.F., Stewart, E.L., Stuart, J.D., Thomas, D.N., Thomson, S.A., Ward, P., Wilson, J.W., Xu, T., Youngman, M.A.(2020) Bioorg Med Chem 28: 115791-115791
- PubMed: 33059303
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115791
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
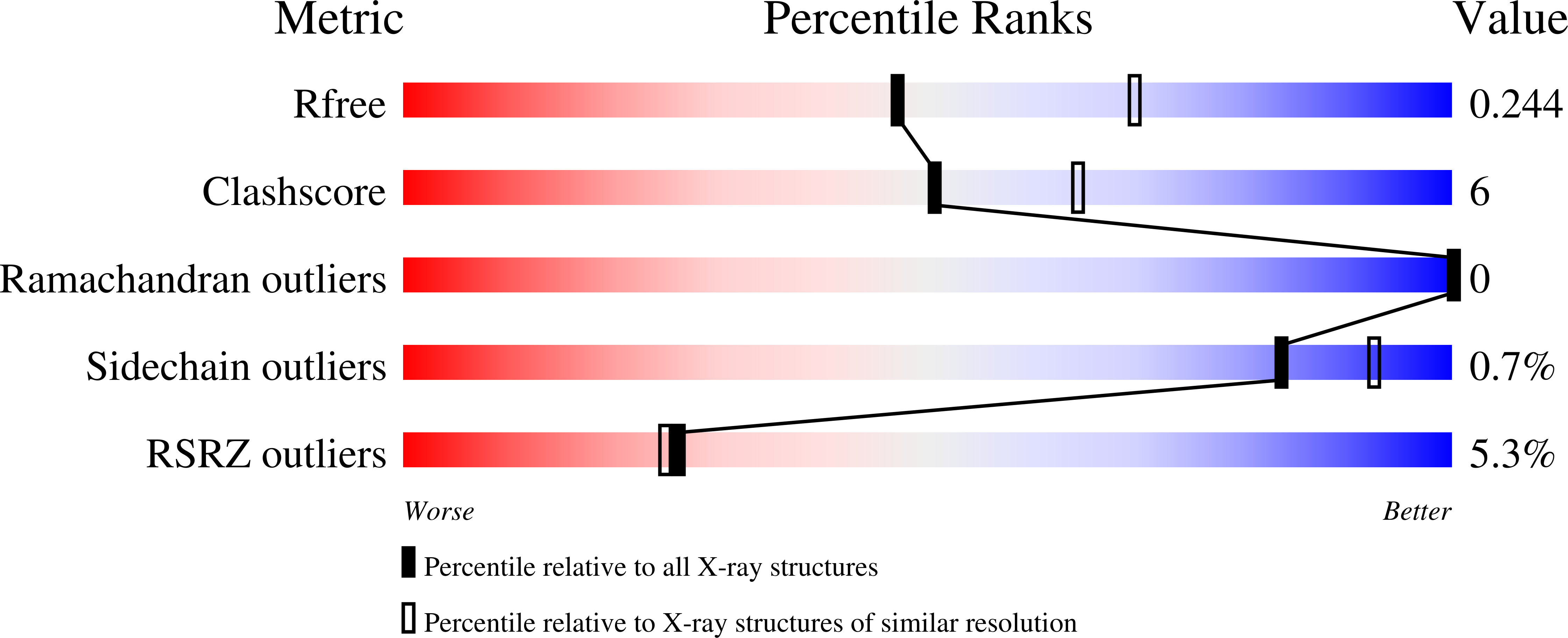
6W58, 6W8H - PubMed Abstract:
GlaxoSmithKline and Astex Pharmaceuticals recently disclosed the discovery of the potent H-PGDS inhibitor GSK2894631A 1a (IC 50 = 9.9 nM) as part of a fragment-based drug discovery collaboration with Astex Pharmaceuticals. This molecule exhibited good murine pharmacokinetics, allowing it to be utilized to explore H-PGDS pharmacology in vivo. Yet, with prolonged dosing at higher concentrations, 1a induced CNS toxicity. Looking to attenuate brain penetration in this series, aza-quinolines, were prepared with the intent of increasing polar surface area. Nitrogen substitutions at the 6- and 8-positions of the quinoline were discovered to be tolerated by the enzyme. Subsequent structure activity studies in these aza-quinoline scaffolds led to the identification of 1,8-naphthyridine 1y (IC 50 = 9.4 nM) as a potent peripherally restricted H-PGDS inhibitor. Compound 1y is efficacious in four in vivo inflammatory models and exhibits no CNS toxicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
GlaxoSmithKline, 5 Moore Drive, P.O. Box 13398, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709, USA.