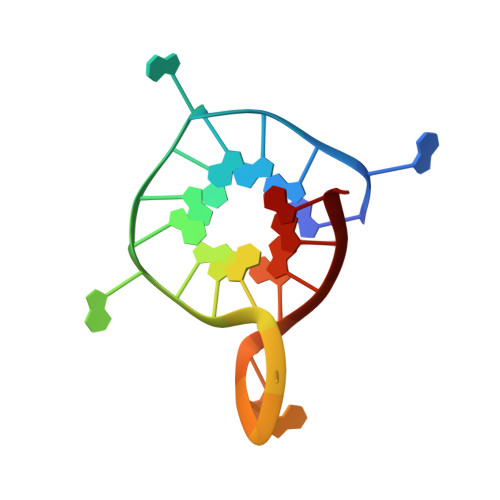
Homopurine guanine-rich sequences in complex with N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX form parallel G-quadruplex dimers and display a unique symmetry tetrad.
Ye, M., Chen, E.V., Pfeil, S.H., Martin, K.N., Atrafi, T., Yun, S., Martinez, Z., Yatsunyk, L.A.(2022) Bioorg Med Chem 77: 117112-117112
- PubMed: 36508994
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2022.117112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8EBO, 8EDP - PubMed Abstract:
DNA can fold into G-quadruplexes (GQs), non-canonical secondary structures formed by π-π stacking of G-tetrads. GQs are important in many biological processes, which makes them promising therapeutic targets. We identified a 42-nucleotide long, purine-only G-rich sequence from human genome, which contains eight G-stretches connected by A and AAAA loops. We divided this sequence into five unique segments, four guanine stretches each, named GA1-5. In order to investigate the role of adenines in GQ structure formation, we performed biophysical and X-ray crystallographic studies of GA1-5 and their complexes with a highly selective GQ ligand, N-methyl mesoporphyrin IX (NMM). Our data indicate that all variants form parallel GQs whose stability depends on the number of flexible AAAA loops. GA1-3 bind NMM with 1:1 stoichiometry. The K a for GA1 and GA3 is modest, ∼0.3 μM - 1 , and that for GA2 is significantly higher, ∼1.2 μM - 1 . NMM stabilizes GA1-3 by 14.6, 13.1, and 7.0 °C, respectively, at 2 equivalents. We determined X-ray crystal structures of GA1-NMM (1.98 Å resolution) and GA3-NMM (2.01 Å). The structures confirm the parallel topology of GQs with all adenines forming loops and display NMM binding at the 3' G-tetrad. Both complexes dimerize through the 5' interface. We observe two novel structural features: 1) a 'symmetry tetrad' at the dimer interface, which is formed by two guanines from each GQ monomer and 2) a NMM dimer in GA1-NMM. Our structural work confirms great flexibility of adenines as structural elements in GQ formation and contributes greatly to our understanding of the structural diversity of GQs and their modes of interaction with small molecule ligands.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Swarthmore College, Swarthmore, PA 19081, United States.
Organizational Affiliation: