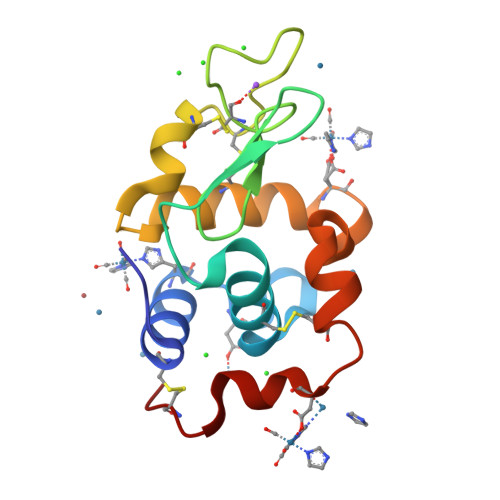
Time-series analysis of rhenium(I) organometallic covalent binding to a model protein for drug development.
Jacobs, F.J.F., Helliwell, J.R., Brink, A.(2024) IUCrJ 11: 359-373
- PubMed: 38639558
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252524002598
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QCU - PubMed Abstract:
Metal-based complexes with their unique chemical properties, including multiple oxidation states, radio-nuclear capabilities and various coordination geometries yield value as potential pharmaceuticals. Understanding the interactions between metals and biological systems will prove key for site-specific coordination of new metal-based lead compounds. This study merges the concepts of target coordination with fragment-based drug methodologies, supported by varying the anomalous scattering of rhenium along with infrared spectroscopy, and has identified rhenium metal sites bound covalently with two amino acid types within the model protein. A time-based series of lysozyme-rhenium-imidazole (HEWL-Re-Imi) crystals was analysed systematically over a span of 38 weeks. The main rhenium covalent coordination is observed at His15, Asp101 and Asp119. Weak (i.e. noncovalent) interactions are observed at other aspartic, asparagine, proline, tyrosine and tryptophan side chains. Detailed bond distance comparisons, including precision estimates, are reported, utilizing the diffraction precision index supplemented with small-molecule data from the Cambridge Structural Database. Key findings include changes in the protein structure induced at the rhenium metal binding site, not observed in similar metal-free structures. The binding sites are typically found along the solvent-channel-accessible protein surface. The three primary covalent metal binding sites are consistent throughout the time series, whereas binding to neighbouring amino acid residues changes through the time series. Co-crystallization was used, consistently yielding crystals four days after setup. After crystal formation, soaking of the compound into the crystal over 38 weeks is continued and explains these structural adjustments. It is the covalent bond stability at the three sites, their proximity to the solvent channel and the movement of residues to accommodate the metal that are important, and may prove useful for future radiopharmaceutical development including target modification.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of the Free State, Nelson Mandela Drive, Bloemfontein, 9301, South Africa.