Asymmetric Synthesis of alpha-Chloroamides via Photoenzymatic Hydroalkylation of Olefins.
Liu, Y., Bender, S.G., Sorigue, D., Diaz, D.J., Ellington, A.D., Mann, G., Allmendinger, S., Hyster, T.K.(2024) J Am Chem Soc 146: 7191-7197
- PubMed: 38442365
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.4c00927
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
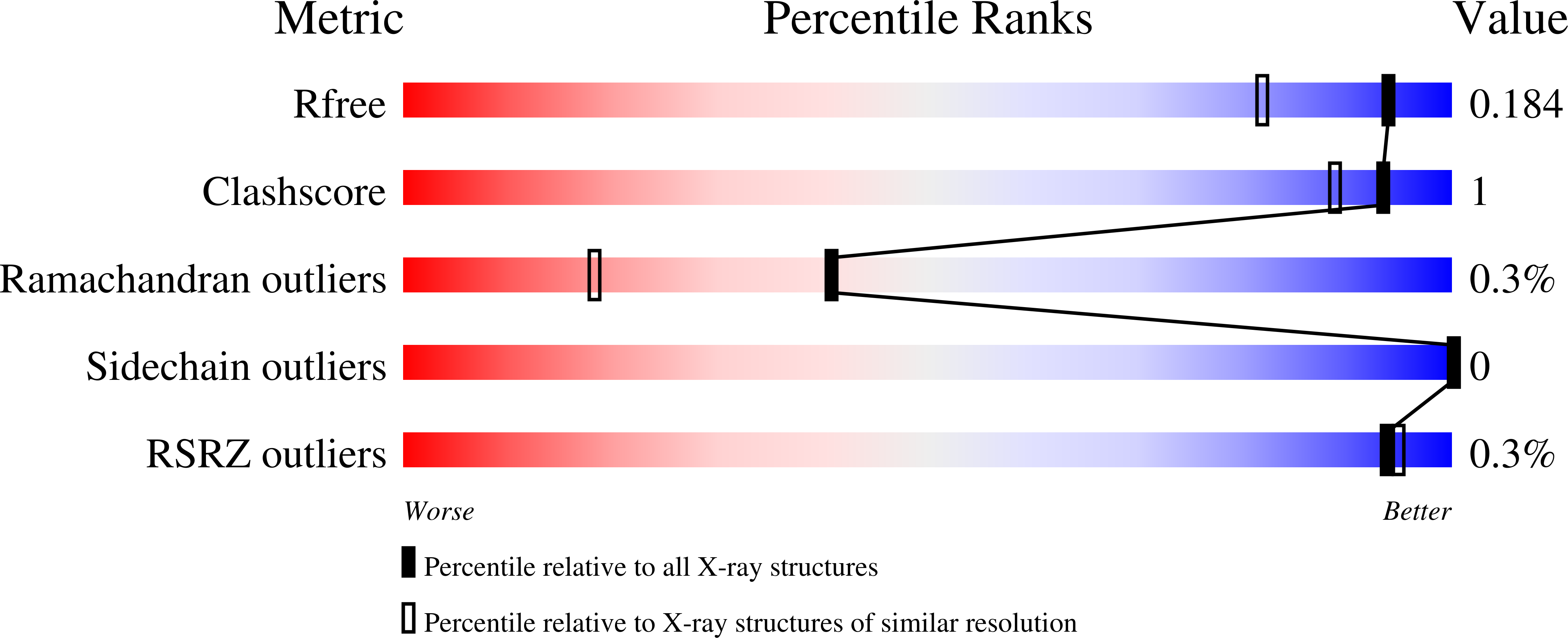
8VCN - PubMed Abstract:
Photoenzymatic intermolecular hydroalkylations of olefins are highly enantioselective for chiral centers formed during radical termination but poorly selective for centers set in the C-C bond-forming event. Here, we report the evolution of a flavin-dependent "ene"-reductase to catalyze the coupling of α,α-dichloroamides with alkenes to afford α-chloroamides in good yield with excellent chemo- and stereoselectivity. These products can serve as linchpins in the synthesis of pharmaceutically valuable motifs. Mechanistic studies indicate that radical formation occurs by exciting a charge-transfer complex templated by the protein. Precise control over the orientation of molecules within the charge-transfer complex potentially accounts for the observed stereoselectivity. The work expands the types of motifs that can be prepared using photoenzymatic catalysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey 08544, United States.