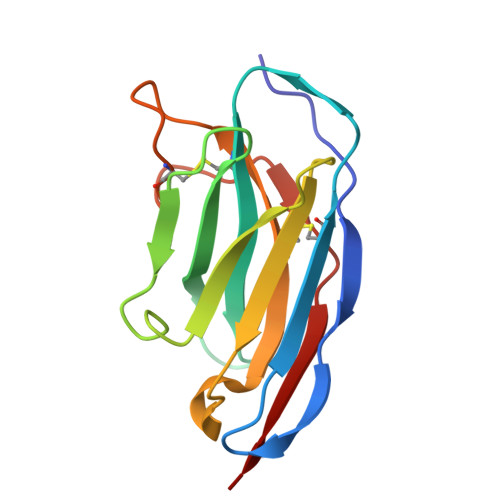
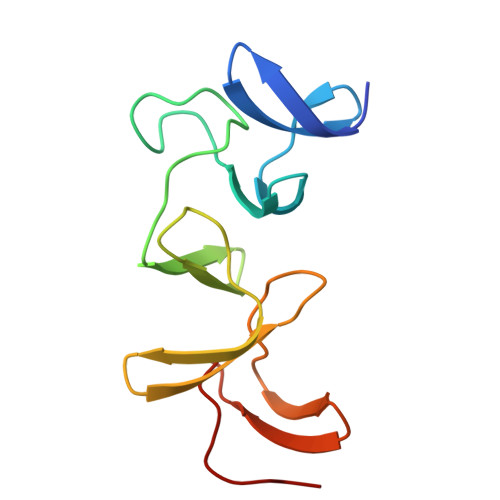
Structural insight into recognition of Clostridioides difficile toxin A by novel neutralizing nanobodies targeting QTIN-like motifs within its receptor-binding domain.
Sluchanko, N.N., Sokolova, I.V., Favorskaya, I.A., Esmagambetov, I.B., Tukhvatulin, A.I., Alekseeva, I.A., Ungur, A.S., Varfolomeeva, L.A., Boyko, K.M., Logunov, D.Y., Gintsburg, A.L., Popov, V.O., Shcheblyakov, D.V., Belyi, Y.F.(2024) Int J Biol Macromol 283: 137910-137910
- PubMed: 39577542
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137910
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YVJ, 8YVO - PubMed Abstract:
Clostridioides difficile causes a large proportion of nosocomial colon infections by producing toxins TcdA and TcdB as key virulence factors. TcdA and TcdB have analogous domain structures with a receptor-binding domain containing C-terminal combined repetitive oligopeptides (CROPs), an attractive target for the development of therapeutic antibodies. Here, we identify and characterize two potent neutralizing single-domain camelid anti-CROPsA antibodies, C4.2 and H5.2, with distinct mechanisms of action. Peptide mapping, high-resolution crystal structures and site-directed mutagenesis revealed that C4.2 and H5.2 nanobodies target the same C-terminal epitope centered on a 2667 QTIN 2670 motif, yet utilize different paratopes. Only for C4.2 is the complex geometry compatible with multisite binding using QTIN-like repeats throughout the CROPsA domain, as supported by Western blotting, ELISA, and SEC-MALS analysis. H5.2 binding is stronger and more selective for the C-terminal epitope than C4.2, although both nanobodies are sufficient to neutralize TcdA individually. The described epitope does not overlap with previously described epitopes of anti-CROPs antibodies and provides new modalities for disease treatment and diagnostics.
- Bach Institute of Biochemistry, Federal Research Centre "Fundamentals of Biotechnology", Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow 119071, Russia; Gamaleya Research Center for Epidemiology and Microbiology, Russian Ministry of Public Health, Moscow 123098, Russia. Electronic address: nikolai.sluchanko@mail.ru.
Organizational Affiliation: