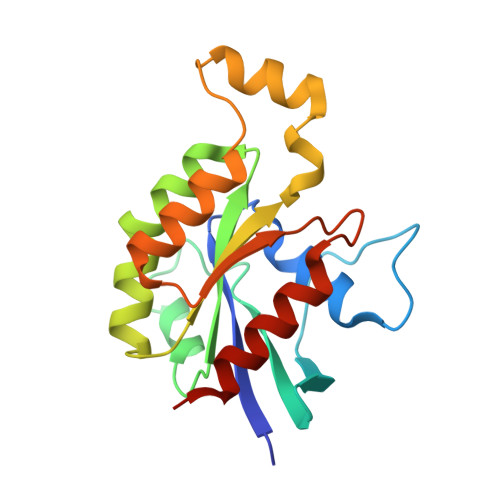
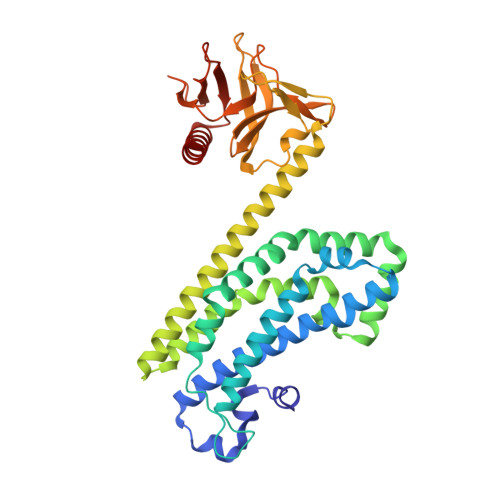
The Crystal Structure of the Rhoa : Akap-Lbc Dh-Ph Domain Complex.
Abdul Azeez, K.R., Knapp, S., Fernandes, J.M.P., Klussmann, E., Elkins, J.M.(2014) Biochem J 464: 231
- PubMed: 25186459
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20140606
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4D0N, 4D0O - PubMed Abstract:
The RhoGEF (Rho GTPase guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor) domain of AKAP-Lbc (A-kinase-anchoring protein-Lbc, also known as AKAP13) catalyses nucleotide exchange on RhoA and is involved in the development of cardiac hypertrophy. The RhoGEF activity of AKAP-Lbc has also been implicated in cancer. We have determined the X-ray crystal structure of the complex between RhoA-GDP and the AKAP-Lbc RhoGEF [DH (Dbl-homologous)-PH (pleckstrin homology)] domain to 2.1 Å (1 Å = 0.1 nm) resolution. The structure reveals important differences compared with related RhoGEF proteins such as leukaemia-associated RhoGEF. Nucleotide-exchange assays comparing the activity of the DH-PH domain to the DH domain alone showed no role for the PH domain in nucleotide exchange, which is explained by the RhoA-AKAP-Lbc structure. Comparison with a structure of the isolated AKAP-Lbc DH domain revealed a change in conformation of the N-terminal 'GEF switch' region upon binding to RhoA. Isothermal titration calorimetry showed that AKAP-Lbc has only micromolar affinity for RhoA, which combined with the presence of potential binding pockets for small molecules on AKAP-Lbc, raises the possibility of targeting AKAP-Lbc with GEF inhibitors.
- *Structural Genomics Consortium, Oxford University, Old Road Campus Research Building, Old Road Campus, Roosevelt Drive, Oxford OX3 7DQ, U.K.
Organizational Affiliation: