Didehydroaspartate Modification in Methyl-Coenzyme M Reductase Catalyzing Methane Formation.
Wagner, T., Kahnt, J., Ermler, U., Shima, S.(2016) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 55: 10630
- PubMed: 27467699
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201603882
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5A0Y, 5A8K, 5A8R, 5A8W - PubMed Abstract:
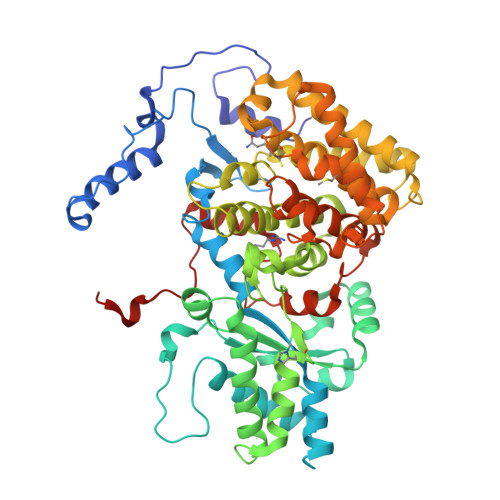
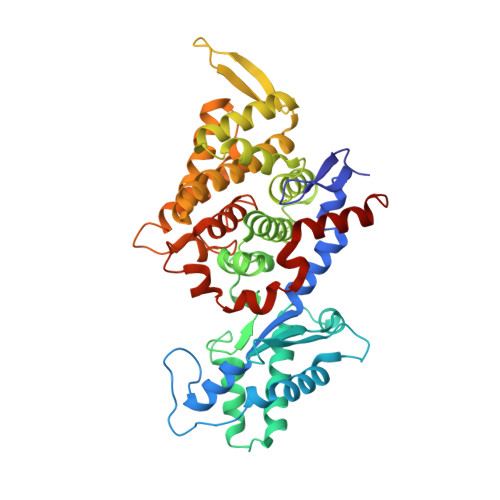
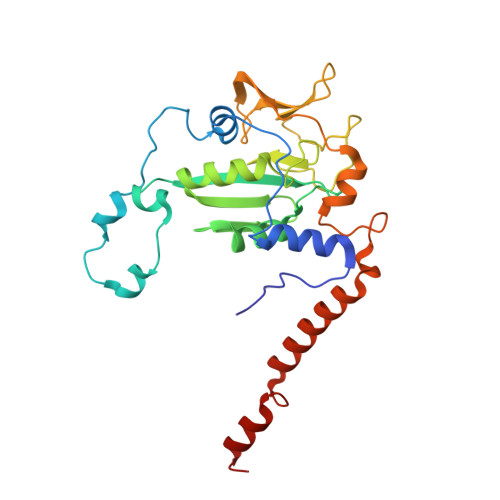
All methanogenic and methanotrophic archaea known to date contain methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR) that catalyzes the reversible reduction of methyl-coenzyme M to methane. This enzyme contains the nickel porphinoid F430 as a prosthetic group and, highly conserved, a thioglycine and four methylated amino acid residues near the active site. We describe herein the presence of a novel post-translationally modified amino acid, didehydroaspartate, adjacent to the thioglycine as revealed by mass spectrometry and high-resolution X-ray crystallography. Upon chemical reduction, the didehydroaspartate residue was converted into aspartate. Didehydroaspartate was found in MCR I and II from Methanothermobacter marburgensis and in MCR of phylogenetically distantly related Methanosarcina barkeri but not in MCR I and II of Methanothermobacter wolfeii, which indicates that didehydroaspartate is dispensable but might have a role in fine-tuning the active site to increase the catalytic efficiency.
- Max-Planck-Institut für terrestrische Mikrobiologie, Karl-von-Frisch-Strasse 10, 35043, Marburg, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: