Structural and Biochemical Characterization of a Trapped Coenzyme a Adduct of Caenorhabditis Elegans Glucosamine-6-Phosphate N-Acetyltransferase 1.
Dorfmueller, H.C., Fang, W., Rao, F.V., Blair, D.E., Attrill, H., Van Aalten, D.M.F.(2012) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 68: 1019
- PubMed: 22868768
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444912019592
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
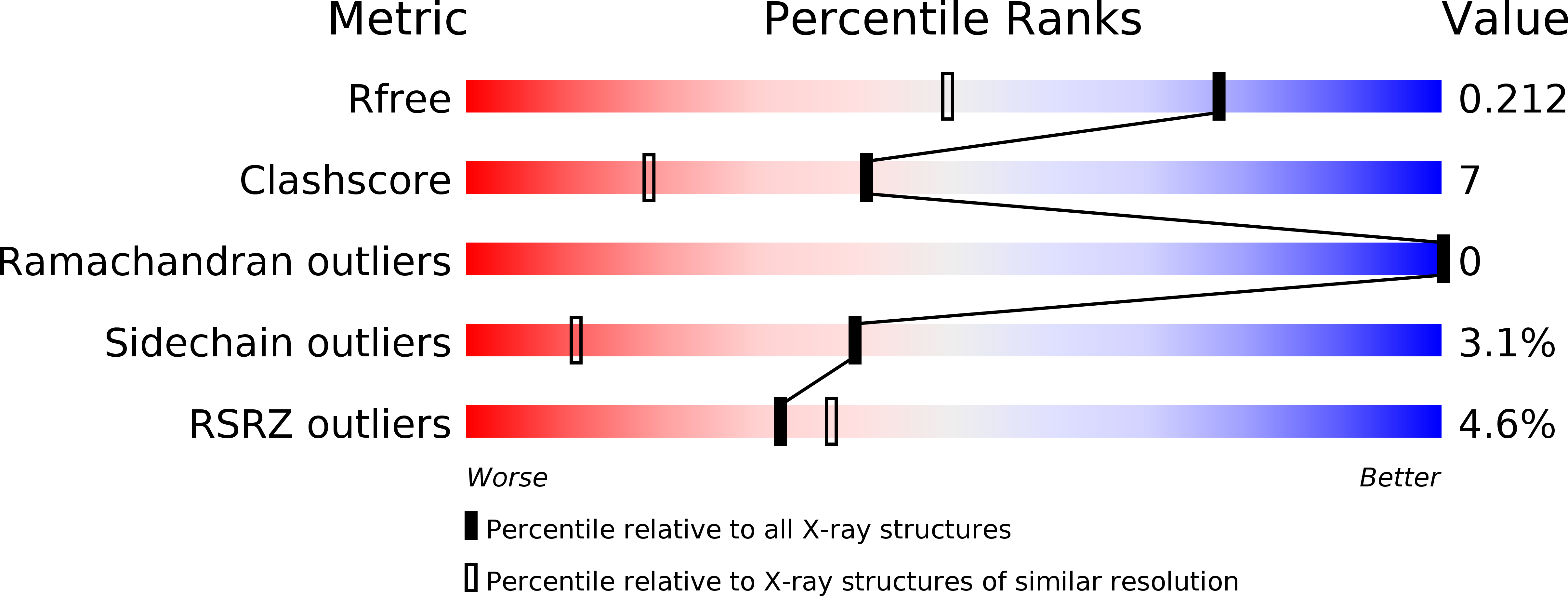
4AG7, 4AG9 - PubMed Abstract:
Glucosamine-6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase 1 (GNA1) produces GlcNAc-6-phosphate from GlcN-6-phosphate and acetyl coenzyme A. Early mercury-labelling experiments implicated a conserved cysteine in the reaction mechanism, whereas recent structural data appear to support a mechanism in which this cysteine plays no role. Here, two crystal structures of Caenorhabditis elegans GNA1 are reported, revealing an unusual covalent complex between this cysteine and the coenzyme A product. Mass-spectrometric and reduction studies showed that this inactive covalent complex can be reactivated through reduction, yet mutagenesis of the cysteine supports a previously reported bi-bi mechanism. The data unify the apparently contradictory earlier reports on the role of a cysteine in the GNA1 active site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Molecular Microbiology, College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dundee DD1 5EH, Scotland.